|
Are your thriller’s sentences front-loaded with filter words? If so, you could be slowing your reader down. This post explains what filter words are, how they affect a sentence and how to decide whether to include them or ditch them.
|
|
Under normal circumstances he would never put his hands on a lady. However, these were not normal circumstances. Not by a long shot.
Ronnie struck the manager just above her right eye with the butt of the .38. A divot the width of a popsicle stick appeared above her eye. Blood spewed from the wound like water from a broken faucet. |
The filter words have gone, and with them the unintended pathological introspection, but the momentum is restored. We're in the moment with Ronnie as he lashes out. It's no less violent but the pace of the prose now mirrors the action authentically.
When filter words make space for reflection
Let’s take a look at another example from Cosby’s Razorblade Tears, this one also from Chapter 2.
The filter phrase is ‘looked at’, and it’s important. Ike is looking hard at what’s in front of him. As will be revealed later, this girl is his murdered son’s daughter. Ike recalls something he’d said to his son a few months earlier: ‘But that little girl, she gonna have it hard enough already. She's half Black. Her mama was somebody you paid to carry her, and she got two gay daddies. So now what?’
Ike and his wife will now be raising the little girl. Cosby wants to focus our attention inward for a moment on Ike’s reflection, and the filter word makes space for that.
While filter words can be effective when they’re used to create a sense of introspection, littering prose with them will be disruptive and pull the reader out of the viewpoint character's headspace. In other words, the psychic or narrative distance will be widened and we’ll feel disconnected from the immediacy of the character’s experience.
For that reason, always use filter words judiciously. In the above example, Cosby offers just a single nudge, and it’s enough.
Summing up
- When filter words front-load a sentence, they’re the first thing a reader notices.
- They destroy momentum and so are often best avoided in pacy action scenes, regardless of their position.
- And even if they do serve a purpose – focusing a reader’s attention inwards on how the viewpoint character acquires the experience they’re reporting (by looking, thinking, feeling etc.) – it's worth keeping their use to a bare minimum. One nudge will likely be enough.
Further reading
- For editors: Fiction editing learning centre
- For authors: Line craft learning centre
- Becoming a Fiction Editor (free booklet for editors)
- Blacktop Wasteland, Cosby, S.A., Headline, 2020
- Editing Fiction at Sentence Level (book for editors and authors)
- Filter words in fiction: Purposeful inclusion and dramatic restriction (blog post)
- Making Sense of ‘Show, Don’t Tell’ (book for editors and authors)
- Narrative Distance: A Toolbox for Writers and Editors (course)
- Razorblade Tears, Cosby, S.A., Headline, 2021
- Switching to Fiction (course for editors)
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
What’s in this post ...
- What is narrative distance?
- Are narrative distance and psychic distance the same thing?
- How is narrative distance related to narrative style?
- Why writers and editors need to learn about narrative distance
- Using a visual framework to understand narrative distance
- Related resources for you to dig into
What is narrative distance?
A narrator is the person who tells the story. They can be a character in the book or an entity that stands outside it.
There can be multiple narrators in a book, too. That allows the author to present events from multiple perspectives.
‘Narrative distance’ describes the space between a novel’s narrator and the reader.
- If we, as readers, feel deeply connected to the narrator and their experience of the fictional world they inhabit, narrative distance is tiny.
- If we feel dislocated from them, more like we’re looking out on the story’s landscape objectively, the narrative distance is wide.
Are narrative distance and psychic distance the same thing?
You might find one or other useful depending on what issues you’re dealing with when you’re writing or editing. I like the word ‘narrative’ because it reminds me what part of the prose I’m dealing with.
Then again, I sometimes use the word ‘psychic’ because it reminds me that although I’m dealing with fiction, and therefore something that’s not real, the narrator within that creative realm still has their own lived experience and a raft of emotions that come with that.
How is narrative distance related to narrative style?
- First-person limited
- Third-person limited
- Third-person objective
- Third-person omniscient
Each of those narrative styles come with a certain degree of distance between the narrator and the reader.
For example, first-person narrations always feel a little more intimate because the pronoun ‘I’ is used. Second-person narrations can feel equally intimate, but in a voyeuristic way.
Third-person narrations – and the pronouns that come with them – are what we’re used to using for those not being directly addressed, so in prose they naturally put space between readers and narrators using the third person.
When we move beyond a framework of narrative style and start to think specifically in terms of narrative distance, we’re able to analyse the effectiveness of prose in a more nuanced and flexible way.
Why writers and editors need to learn about narrative distance
Perhaps you’ve never noticed before, and if that’s the case, the author and their editor have done a great job because the movement is seamless.
If that movement is jarring and too obvious, it could be an indication that narrative distance isn’t being controlled sufficiently. Editors and writers who can recognize narrative distance and evaluate its effectiveness are better equipped to solve the problem, and justify their solutions.
Using a visual framework to understand narrative distance
My solution was to structure my own learning as a visual framework. I presented that framework at the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading’s annual conference in September 2021 and then for the Society of Authors in October 2021.
The framework I shared at those two events garnered fabulous reviews and convinced me to record a webinar that everyone could access.
Narrative Distance: A Toolbox for Writers and Editors is available now to anyone who wants to lift the curtain on narrative distance and use it to craft prose that offers a better reader experience.
Use the button below to find out what’s included in the course.
|
If you’re a CIEP member, don’t forget that you can save 20% on all my courses. Log in to Promoted courses · Louise Harnby’s online courses. Then enter the coupon code at my checkout.
|
Related resources for you to dig into
- Blog post: 7 reasons why I’m not the right editor for you
- Blog post: How to avoid repeating ‘I’ in first-person writing
- Blog post: How to show the emotions of non-viewpoint characters
- Blog post: What’s the difference between a viewpoint character and a protagonist?
- Book: Editing Fiction at Sentence Level
- Book: Making Sense of Point of View
- Course: How to Write the Perfect Fiction Editorial Report
- Course: Switching to Fiction
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
In this post ...
- Clutter check #1: Reviewing filter words
- Clutter check #2: Reviewing speech tags
- Clutter check #3: Reviewing action beats
Clutter check #1: Review your filter words
Too many filter words that explain this sensory behaviour in action can make prose feel told rather shown, and increase narrative distance.
Examples include ‘noticed’, ‘seemed’, ‘spotted’, ‘saw’, ‘realized’, ‘felt’, ‘thought’, ‘wondered’, ‘believed’, ‘knew’ and ‘decided’.
Removing them focuses the reader’s gaze outwards on what is being experienced.
Sometimes an author wants an inward focus, but it’s often the case that the reader will assume that an odour is being smelled, a view is being seen, a thought is being thought, and knowledge is being known.
Review your narrative and consider whether the removal of a filter word would make the prose shorter and more immersive.
Here are some examples:
|
WITH FILTER
|
FILTER REMOVED
|
|
Danni knew there was a door in the back of the hut that led into the woods. She could make her escape there.
[Reader’s gaze focuses inwards on Danni’s doing the action of knowing.] |
There was a door in the back of the hut that led into the woods. She could make her escape there.
[Reader assumes it’s Danni doing the knowing since she’s the viewpoint character, and focuses outwards on the solution – the door.] |
|
The backdoor – it leads to the woods, Danni thought.
[Reader’s gaze focuses inwards on Danni’s doing the action of thinking.] |
The backdoor – it leads to the woods.
[Reader assumes the thought belongs to Danni, and focuses on the substance of the thought.] The backdoor – it led to the woods. [This alternative uses free indirect style; it frames the thought in the novel’s base tense and narrative style – third-person past.] |
|
He flung open the door and saw the gunman standing over by the window, rifle trained on the street below.
[Reader’s gaze focuses inwards on the man’s doing the action of seeing.] |
He flung open the door.
The gunman stood over by the window, rifle trained on the street below. [Reader assumes it’s the man doing the seeing since he’s the viewpoint character, and focuses outwards on the gunman.] |
Clutter check #2: Review speech tags
Review your dialogue tags and consider the following:
- Is the tag necessary?
- Is the tag taking centre stage?
- Is the tag illogical?
If there are only two characters in a scene, it might be obvious who’s speaking, which gives the author space to introduce reminder nudges only now and then.
|
ALL THE TAGS!
|
REDUCED TAGGING
|
|
‘There’s a door at the back of the hut,’ Danni said.
‘You’re sure it isn’t locked?’ I said. ‘No,’ she said. ‘Trish never locks it. Not since the fire.’ ‘And that’ll get us into the woods?’ I said. ‘Yup. There’s a track. It’s overgrown but I know the way. Used it all the time when I was young and foolish,’ she said. ‘What do you mean was?’ I said. ‘You’re too funny,’ she said, and pulled a face. |
‘There’s a door at the back of the hut,’ Danni said.
‘You’re sure it isn’t locked?’ ‘No. Trish never locks it. Not since the fire.’ ‘And that’ll get us into the woods?’ ‘Yup. There’s a track. It’s overgrown but I know the way. Used it all the time when I was young and foolish.’ ‘What do you mean was?’ I said. Danny pulled a face. ‘You’re too funny.’ |
Showy speech tags scream their presence from the page, and shift the reader’s attention away from the dialogue and onto the tag. They often tell what the dialogue’s already shown, and indicate a lack of trust in the reader to get the speech. Examples include ‘exclaimed’, ‘opined’, ‘commanded’
|
TAG TAKES CENTRE STAGE
|
DIALOGUE TAKES CENTRE STAGE
|
|
‘Watch out!’ Danni warned.
|
‘Watch out!’ Danni said.
|
|
‘Yup. There’s a track. It’s overgrown but I know the way. Used it all the time when I was young and foolish.’
‘What do you mean was?’ I joked. |
‘Yup. There’s a track. It’s overgrown but I know the way. Used it all the time when I was young and foolish.’
‘What do you mean was? |
|
EXPRESSION TAG
|
ACTION BEAT
|
|
‘No,’ Danni grimaced. ‘Trish never locks it. Not since the fire.’
|
‘No.’ Danni grimaced. ‘Trish never locks it. Not since the fire.’
|
|
EXPRESSION TAG
|
SPEECH TAG
|
|
‘Yup. There’s a track. It’s overgrown but I know the way. Used it all the time when I was young and foolish.’
‘What do you mean was?’ I laughed. |
‘Yup. There’s a track. It’s overgrown but I know the way. Used it all the time when I was young and foolish.’
‘What do you mean was?’ I said. |
Clutter check #3: Review action beats
They key to effective use is ensuring they amplify dialogue rather than interrupt it.
Think about movies. On the screen, all the actors movements and gestures are visible. Replicating this detail in a novel can be invasive and pull the reader away from what’s being unveiled through the speech.
While action beats are superb backdoors into the emotional space of non-viewpoint characters, the dialogue should be where the main action is taking place. If it’s not, what might be required is a reworking of the dialogue, not the introduction of more action beats.
Instead of mimicking the screen experience, use action beats to show what the dialogue doesn’t convey. That needn’t mean including them with every turn. Great dialogue doesn’t need to be anchored every time a character opens their mouth. A purposeful nudge now and then will be enough.
Watch out in particular for prose that’s overloaded with mundane action beats – legs stretching, fingers raking through hair, raised eyebrows, arms folding, fingers steepling.
Review your action beats:
- Do they tell the reader something the dialogue doesn’t or are they mundane details that a reader could imagine?
- Are they infrequent nudges or are they littering the dialogue at every turn of speech?
- Could the mood conveyed by the action beat be conveyed better by improving the dialogue?
Getting rid of the dull and redundant ones will reduce your word count. And what’s left on the page will be more engaging.
|
ACTION BEATS THAT INTERRUPT DIALOGUE
|
ACTION BEATS THAT AMPLIFY DIALOGUE
|
|
Danni pointed at the back of the cellar. ‘Over there. The door. It leads to the woods.’
‘You’re sure it isn’t locked?’ Max rubbed his forehead. ‘Maybe we need a Plan B.’ ‘No.’ Her brow furrowed. ‘Trish never locks it. Not since the fire.’ Max tilted his head. ‘The fire? What happened?’ ‘It was years ago.’ She waved his question away and jabbed a finger towards the door again. ‘Out back there’s a track. It’s overgrown but I know the way. Used it all the time when I was young and foolish.’ ‘What do you mean was?’ he said, and smirked. She pulled a face. ‘You’re too funny.’ |
Danni pointed at the back of the cellar. ‘Over there. The door. It leads to the woods.’
‘You’re sure it isn’t locked?’ Max said. ‘I dunno, maybe we need a Plan B.’ ‘No. Trish never locks it. Not since the fire.’ ‘The fire? What—’ ‘It was years ago. Whatever. Focus. Out back there’s a track. It’s overgrown but I know the way. Used it all the time when I was young and foolish.’ ‘What do you mean was?’ She pulled a face. ‘You’re too funny.’ |
Summing up
However, if they’re mundane or interruptive clutter that can be assumed, leave them out so we can focus on the words that really matter.
Related reading
- 3 reasons to use free indirect speech in your crime fiction
- Author writing resources
- Becoming a Fiction Editor (free booklet for editors)
- Dialogue tags and how to use them in fiction writing
- Editing Fiction at Sentence Level (book for editors and authors)
- Filter words in fiction
- Making Sense of ‘Show, Don’t Tell’ (book for editors and authors)
- Switching to Fiction (course for editors)
- Tips on lean writing
- What are action beats and how can you use them in fiction writing?
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
What’s in this post
- to show rather than tell internal experience
- to decelerate reading speed
- to emphasize key information
- to create clutter-free immediacy
- to deliver suspenseful chapter finales
Showing rather than telling internal experience
The staccato rhythm of one-line paragraphs is interruptive, both rhythmically and visually. Each short line is its own single beat, one that’s structurally visible on the page. Every time the reader moves onto the next, they take mental breath.
Because the lines are short, the breaths come quickly, and it’s there that the author can show rather than tell a character's internal experience in a way that's rich in mood and voice.
In this excerpt from Recursion by Black Crouch, p. 317 (Pan, 2019), look at how the structure of those two initial short lines in bold mirrors the meaning of the words.
|
The memories arrive in a blink.
One moment nothing. The next, he knows exactly where he is, the full trajectory of his life since Helena found him, and exactly what the equations on the blackboard mean. Because he wrote them. They're extrapolations of the Schwarzschild solution, an equation that defines what the radius of an object must be, based upon its mass, in order to form a singularity. That singularity then forms an Einstein-Rosen wormhole that can, in theory, instantaneously connect far-flung regions of space and even time. |
One minute the memories aren’t there; the next they are. The beat of their arrival is reflected in the way the prose is formatted. We’re therefore shown how the viewpoint character experiences the lightning-speed download of knowledge, and as a result we feel it all the more intensely.
Decelerating reading speed
Such speedy reading can lead to skimming because we relax into the flow of the narrative. One-line paragraphs, however, stand out because they contrast so starkly with the longer passages, surrounded as they are by so much white space.
Text that stands out begs for our attention and forces us to slow down and focus on each word. And that means it’s not only the rhythm of the prose that’s changed; so has the rhythm of how we’re interacting with it as readers.
Take a look at this example on p. 470 of The Good Daughter by Karin Slaughter (HarperCollins, 2017).
|
There was more tapping, more tracking, and then colours on the screen were almost too much. The blacks were up so far that gray spots bubbled through the midnight fields.
Charlie suggested, “Use the blue on the lockers as a color guide. They’re close to the same blue as Dad’s funeral suit. Ben opened the color chart. He clicked on random squares. “That’s it,” Charlie said. “That’s the blue.” “I can clean it up more.” He sharpened the pixels. Smoothed out the edges. Finally, he zoomed in as close as he could without distorting the image into nothing. “Holy shit,” Charlie said. She finally got it. Not a leg, but an arm. Not one arm, but two. One black. One red. A sexual cannibal. A slash of red. A venomous bite. They had not found Rusty’s unicorn. They had found a black widow. |
The non-bold text is what we’re most used to seeing. It makes for a comfortable, leisurely, skimmable read. But when we get to the bold single-line paragraphs, the contrast is visible on the page. Our reading pace decelerates and our attention zooms in on every word.
Emphasizing key information
Because the one-liner stands out, it’s an opportunity for centre-staging. Here’s a great example from Harlan Coben’s Win, p. 38 (Century, 2021).
|
Respect, yes. Bow, no. I also don’t use these techniques,
per the platitude, “only for self-defense,” an obvious untruth on the level of “the check is in the mail” or “don’t worry, I’ll pull out.” I use what I learn to defeat my enemies, no matter who the aggressor happens to be (usually: me). I like violence. I like it a lot. I don’t condone it for others. I condone it for me. I don’t fight as a last resort. I fight whenever I can. I don’t try to avoid trouble. I actively seek it out. After I finish with the bag, I bench-press, powerlift, squat. When I was younger, I’d have various lifting days—arm days, chest days, leg days. When I reached my forties, I found it paid to lift less often and with more variety. |
Coben wants us to know something about his protagonist Windsor Horne Lockwood III, something we might find distasteful and hard to fathom. Nevertheless, it’s central to the characterization; Win’s actions throughout the novel don’t make sense unless we know this. Coben ensures we don’t miss it.
Creating clutter-free immediacy
This can reduce narrative distance – the space between the reader and the viewpoint character.
Here’s beautiful example from p. 296 of The Cold Cold Ground by Adrian McKinty (Serpent’s Tail, 2012)
|
“You had to stick your fucking neb in, didn’t ya? You had to open your big yapper. Can’t you fucking take a hint? After all them ciggies we give you too,” he said.
He raised the gun. I closed my eyes. Held my breath. A bang. Silence. When I opened my eyes again Bobby Cameron was staring at me and shaking his head. Billy White was dead to my left with the back of his head blown off. |
The narration is first person, so it’s already immersive. But the one-line paragraphs in bold drive us deeper into Sean Duffy’s experience. There’s no fluff, no filtering, no cluttering description.
Each moment of the action is presented oh so precisely, slamming us into the now of the novel – the weapon being raised, Duffy’s physical response, then what he hears: first a bang, then nothing.
In five lines and fourteen words, McKinty shows us something powerful – that he trusts us to get it. We don’t know for sure what Duffy is feeling. It could be sadness, terror, anger, resignation, or a combination of some or all those things.
The author’s had the courage to leave it to us, to allow us to imagine what this moment means internally for Duffy, rather than forcing us one way or another. In doing so, we get to be Duffy for a while rather than a fly on the wall. The narrative distance is so small, it’s barely perceptible.
Delivering suspenseful chapter finales
When that yearning is encapsulated in one line, it stands out and demands that we turn the page.
Here are the final two paragraphs from p. 132 of David Rosenfelt’s Open and Shut (Grand Central Publishing, 2002)
|
The next morning, to my undying shame, I did not withdraw my request. I had the time of my life at camp that summer, and I know now that my father, so desperate for me to go that he was in terrible pain, had millions of dollars that he refused to touch.
Money that he did not make delivering newspapers. [Chapter ends] |
There is only one question on the reader’s mind as the chapter closes: So how did his father make all that money?
And because the answer lies beyond – maybe in the next chapter, maybe right at the end of the book – we turn the page.
Why less is more
One-liners pack the biggest punch when they’re used now and then as a tool with which to vary the pulse of your prose and deepen your reader’s immersion in the world you’ve created.
Save them for best so that they stand out.
More writing and editing resources
|
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
What’s covered in this post
- Why reduce the ‘I’
- Why ‘I’ still has a place front and centre
- Focusing on the exterior rather than the interior
- Reducing the use of filter words
- Removing speech and thought tags
- Applying the principles of free indirect speech
- Taking the 'I' out of introspection
- Balancing ‘I’ with ‘we’
Why reduce the ‘I’
Too much ‘I’ is a tap on the shoulder, one that says to the reader, ‘Just in case you’ve forgotten who the narrator is, here are lots of reminders.’
The consequence is that readers are pulled away. And that can actually increase rather than reduce narrative distance.
Why ‘I’ still has a place front and centre
However, they don’t rely on a first-person pronoun to convey experience, thought, speech and action. Below, I'll show you some examples – ones that ensure the intimacy of the narration style is left intact.
And so while we don’t want to obliterate ‘I’, because avoiding it completely would render the prose awkward, inauthentic and overworked, too much ‘I’ can be repetitive and interruptive. What’s required is a balance.
This post aims to offer you choice – fitting alternatives that retain intimacy and immediacy when you’re concerned you’ve overdone it.
1. Focus on the exterior rather than the interior
A little peppering in a more objective report will suffice because the reader knows that it’s coming from the narrator, and only the narrator. It has to be.
And while writers can make space to explore the viewpoint character’s emotional behaviour, the exterior world is what grounds their experience in the novel’s physical world. It gives the novel substance, and the reader something to bite into.
Instead of focusing on who’s doing the reporting, shift the prose towards what’s being reported.
What and who else is in the scene? Why are they there? How do they behave? What do they look like? This information can be reported without ‘I’ so that the reader experiences the physical world within which the narrator is operating.
Here’s an example from To Kill a Mockingbird (Harper Lee, Pan, 1974, p. 11).
|
Maycomb was an old town, but it was a tired old town when I first knew it. In rainy weather the streets turned to red slop; grass grew on the sidewalks, the court-house sagged in the square. Somehow, it was hotter then; a black dog suffered on a summer’s day; bony mules hitched to Hoover carts flicked flies in the sweltering shade of the live oaks on the square. Men’s stiff collars wilted by nine in the morning. Ladies bathed before noon, after their three o’clock naps, and by nightfall were like soft tea-cakes with frostings of sweat and sweet talcum.
People moved slowly then. They ambled across the square, shuffled in and out of the stores around it, took their time about everything. A day was twenty-four hours long but seemed longer. There was no hurry, for there was nowhere to go, nothing to buy and no money to buy it with, nothing to see outside the boundaries of Maycomb County. But it was a time of vague optimism for some of the people: Maycomb County had recently been told that it had nothing to fear but fear itself. |
Notice the (almost) absence of ‘I’. Scout – our narrator – tells us about the town she lived in: Maycomb. The recollection is hers certainly – ‘when I first knew it’ anchors it as such. It’s therefore intimate.
And yet because there’s only one I-nudge, we’re allowed enough emotional distance to step back and pan, like a roving camera, across Maycomb’s vista. We’re dislocated from Scout’s doing the experiencing and encouraged instead to focus on what she’s experiencing.
What’s happening here is a shift from the subjective to the objective.
Here’s an example of a short excerpt that’s subjective. The focus is on the I-narrator.
And here’s the real excerpt from David Rosenfelt’s Play Dead (Grand Central, 2009, p. 19). Now the focus is objective, yet in no way does this distance us from the centrality of the first-person narrator’s experience. We’re still deep in his head.
2. Reduce the use of filter words
Examples include noticed, seemed, spotted, saw, realized, felt, thought, wondered, believed, knew, and decided.
Filter words focus the reader’s gaze inwards (interior focus) on the manner through which the viewpoint character experiences the world – the how.
They come with a pronoun: I saw, they believed, we decided, she knew, he noticed.
By removing filter words, the reader’s gaze is shifted outwards (exterior focus) and onto what is being experienced. That can make for a more immersive read. Plus, the omission means we say goodbye to their accompanying pronoun: 'I'.
Here are a few examples to give you a flavour of how you might recast in a way that avoids first-person filtering.
|
‘I’ plus filter word. Reader’s gaze is inwards, on the how
|
Recast: Reader’s gaze drawn outwards towards the what
|
|
I recall the argument we had last week.
|
Last week’s argument is still fresh in my mind.
|
|
I recognized the man’s face.
|
The man’s face was familiar.
|
|
I saw the guy turn left and dart into the alley.
|
The guy turned left and darted into the alley.
|
|
I spotted the red Chevy from yesterday parked outside the bank.
|
There, parked outside the bank, was the same red Chevy from yesterday.
|
|
I still feel ashamed about the vile words I unleashed even after all these years.
|
The vile words I unleashed still have the power to bathe me in shame even after all these years.
|
3. Remove speech and thought tags
This will work best if there are no more than two characters. Most writers don’t extend the omission for more than a few back-and-forths before they introduce a reminder tag or an action beat.
Watching out for unnecessary tags is good practice regardless of narration style, but with a first-person narration it’s a particularly efficient way to declutter ‘I’-heavy prose.
Take a look at this excerpt from David Rosenfelt’s Play Dead, pp. 194–5. There are two characters in this scene: Andy Carpenter, the protagonist and narrator, and Sam Willis, the non-POV character on the other end of the phone.
“The woman's name is Donna Banks. She lives in apartment twenty-three-G in Sunset Towers in Fort Lee. I don't have the exact address, but you can get it.”
“Pretty swanky apartment,” he says.
“Right. I want you to find out the source of that swank.”
“What does that mean?”
“I want to know how she can afford it. She doesn't work, and she's the widow of a soldier. Maybe her name is Banks because her family owns a bunch of them, but I want to know for sure.”
“Got it.”
“No problem?” I ask. I'm always amazed at Sam's ability to access any information he needs.
“Not so far. Anything else?”
“Yes. I left her apartment at ten thirty-five this morning. I want to know if she called anyone shortly after I left, and if so, who.”
“Gotcha. Which do you want me to get on first? Although neither will take very long.”
“I guess her source of income.”
“Then say it, Andy.”
“Say what?”
“Come on, play the game. You're asking me to find out where she gets her cash. So say it.”
“Sam …”
“Say it.”
“Okay. Show me the money.”
“Thatta boy. I'll get right on it.”
The exchange involves 19 speech elements within the thread, but only 3 speech tags, and only one of those marks our first-person narrator.
At no point do we lose track, and at no point are we distracted by repetitive ‘I said’s.
4. Apply the principles of free indirect speech
In a nutshell, free indirect speech offers the essence of first-person dialogue or thought but through a third-person viewpoint. The character’s voice takes the lead, but without the clutter of speech marks, speech tags, italic, or other devices to indicate who’s thinking or saying what.
Here’s an example of third-person narration. Notice the filter words ‘glanced’ and ‘noticed’, the italic present-tense thought, and the thought tag:
Let’s change that to a first-person narration. The filter words are still there and there’s a thought tag with the ‘I’ pronoun.
Here’s what the third-person version could look like in free indirect style. The filter words and tags are gone. It feels like a first-person thought but the base tense and third-person narration remain intact.
And now the first-person version. All I’ve done is swapped out the pronoun ‘his’ for ‘my’.
5. Take the ‘I’ out of introspection
However, when prose is littered rather than peppered with constructions such as I wasn’t sure if, I didn’t know whether, I wondered if, it can feel muddled and be laborious to read. The reader might respond: Well, of course you’re wondering. Who else could it be? You’re the narrator.
Worse, readers might think the narrator’s rather self-absorbed and unsure of themselves. While that might be necessary now and then, it’s problematic if it’s a staple because a narrator who’s always focused on themselves, and who never instils confidence in us, can’t tell the story as effectively.
Look out for ‘I’-centred introspection and experiment with statements and questions that allow the ‘I’ to be assumed.
Here are a few examples to show you how it might work.
|
‘I’-centred introspection
|
‘I’-less introspection
|
|
I wasn’t sure if Shami was a reliable witness but I couldn’t afford to ignore her, given what she’d divulged.
|
Was Shami a reliable witness? Maybe, maybe not. She couldn’t be ignored given what she’d divulged.
|
|
I still didn’t know who the killer was.
|
The killer’s identity was still a mystery.
|
|
I wondered whether Shami was a reliable witness.
|
Shami might or might not be a reliable witness.
Shami’s reliability as a witness was hardly a given. Shami’s reliability as a witness was questionable. |
6. Balance ‘I’ with ‘we’
This is an opportunity to frame the narrative around ‘we’ rather than just ‘I’.
Here’s an excerpt from To Kill a Mockingbird (p. 162) in which Scout, Harper Lee’s first-person narrator, frames the recollection around not just her own experience but those of the people she was hanging out with.
A wagonload of unusually stern-faced citizens appeared. When they pointed to Miss Maudie Atkinson's yard, ablaze with summer flowers, Miss Maudie herself came out on the porch. There was an odd thing about Miss Maudie – on her porch she was too far away for us to see her features clearly, but we could always catch her mood by the way she stood. She was now standing arms akimbo, her shoulders drooping a little, her head cocked to one side, her glasses winking in the sunlight.
The effect is powerful because we’re shown rather than told a sense of her belonging, of her being in a group, of the togetherness of that experience. And that intensifies our immersion in her world.
Summing up
Try recasting sentences that start with ‘I’ more objectively, so that the focus is on the what – the emotion, the object, the person, the action and so on – rather than the sense being used to experience it or the I-narrator doing the experience.
Use the principles of free indirect speech to reduce your ‘I’ count. It’s a tool that encourages a narrowing of narrative distance to such a degree that the reader feels deeply connected to the viewpoint character – more like we’re reading a thought than straight narrative.
As for speech and thought tags, you might not need as many as you think. The speaker can usually be identified without them if there are only two people in the conversation. Removing redundant tags is worth considering whichever narration style you’re writing in.
Related resources
- 3 reasons to use free indirect speech
- 6 ways to improve your novel right now
- Author resource library (includes links to free webinars)
- Editing Fiction at Sentence Level: A Guide for Beginner and Developing Writers
- Filter words in fiction: Purposeful inclusion and dramatic restriction
- Making Sense of Point of View: Transform Your Fiction 1
- What is head-hopping, and is it spoiling your fiction writing?
- Switching to Fiction: Course for new fiction editors
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
Why speech in a novel is different
Every line of dialogue should have a purpose. If it doesn’t, it probably shouldn’t be in your book.
It can take courage to remove words you've spent an age crafting but as I hope to show in the example below, readers don't need every little detail. Less is so often more!
A three-pronged approach to dialogue
When we focus on those three things, we avoid dull dialogue – conversations about the weather, how someone takes their tea or coffee, and courtesy statements such as ‘Hi, how are you?’
Voice tells us who characters are, what makes them tick – their fears, frustrations, hopes and dreams, identity, preferences.
Perhaps their speech is abrupt, rude, measured, polite, sweary or seductive.
When we change the way a character speaks, we change their voice. And that means we change them.
Characters can show us how they’re feeling via their dialogue.
Emotionally evocative speech allows readers to access the internal experience of a non-viewpoint character. And that makes it a powerful tool.
Perhaps their speech is abrupt, assertive, hesitant, forceful, pleading. Using the right words means the speech tags and narrative won’t need to be cluttered with further explanation.
Intention is another way of framing subtext. How characters speak tells us what they want.
Perhaps they’re asking questions for the purpose of discovery and understanding whodunit (doctors, lawyers, PIs and police officers regularly use dialogue in novels to this end). Dialogue can express a multitude of motivations.
Ask yourself what your character wants every time they open their mouth.
Example: Real but mundane dialogue
“Hi, Kevin,” I say.
“Hey, Andy. How you doin’?”
“Not too bad, thanks. Christ, it’s cold out though. I need something to warm me up. Gonna grab a coffee. Want one? Laurie, you?”
Kevin nods.
Laurie says, “Please. Milk and sugar.”
“So Kevin,” I say as I hand around the drinks, “we need to talk about Petrone.”
It’s the first chance I’ve had to tell Kevin about my meeting with the guy. I fill him in. When I get to the part where Petrone denied trying to have me killed, Kevin asks, “And you believed him?”
“I did.”
“Just because that’s what he said?”
I nod. “As stupid as it might sound, yes. I’ve had dealings with him before, and he’s always told me the truth, or nothing at all. And he had nothing to gain by lying.”
“Andy, the guy has had a lot of people murdered. How many confessions has he made?”
Were you enthralled by the welcome and refreshments section, or did you just wish we could get to the point? I think I know the answer!
The slimmed-down version
These meetings are basically of dubious value, since all we seem to do is list the things we don’t understand in our preparation for a trial we don’t know will even take place.
It’s the first chance I’ve had to tell Kevin about my meeting with Petrone. I fill him in. When I get to the part where Petrone denied trying to have me killed, Kevin asks, “And you believed him?”
“I did.”
“Just because that’s what he said?”
I nod. “As stupid as it might sound, yes. I’ve had dealings with him before, and he’s always told me the truth, or nothing at all. And he had nothing to gain by lying.”
“Andy, the guy has had a lot of people murdered. How many confessions has he made?”
What readers don’t care about
And so he leaves all of that out and lets the reader imagine that this stuff took place. And it’s enough. In the published novel, as opposed to the version I butchered, the first line of speech is “And you believed him.”
With that, we’re straight into Kevin’s incredulity and concern, and his desire to understand what the team is dealing with in regard to Petrone.
Meanwhile, Andy has his lawyer hat on. His initial reply is succinct, so that we are left in no doubt about his belief that Petrone was telling the truth, and that he is determined to reassure Kevin.
This is no-messing dialogue that focuses on story, not whether the speech is what we might actually hear – in its entirety – in real life.
It’s an excellent example of an author ensuring that every word counts and that there’s no bus-stop-talk filler.
Summing up
- Is every line relevant to the story?
- Is the character speaking with purpose or taking up ink/pixels on the page?
- Can mundane chitchat be removed without damaging sense and flow?
- Could the dull stuff be replaced with speech that deepens character?
Want the booklet version of this post? It's available on my Dialogue resources library. Click on the cover below to hop over to the page. Once you're there, choose the Booklets icon.
More fiction editing resources for authors and editors
- Editing Fiction at Sentence Level
- Making Sense of ‘Show, Don’t Tell’
- Making Sense of Point of View
- Making Sense of Punctuation
- How to Write the Perfect Fiction Editorial Report
- Switching to Fiction
- The Differences Between Developmental Editing, Line Editing, Copyediting and Proofreading (free webinar)
- How to Punctuate Dialogue in a Novel (free webinar)
- Resource library: Dialogue and thoughts
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
FIND OUT MORE
> Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
> Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
> Learn: Books and courses
> Discover: Resources for authors and editors
Review your novel for 6 common problems. None involve major rewriting, just relatively gentle recasts that will improve your prose significantly, and make your reader's experience more immersive.
1. Assess invasive adverbs
2. Remove redundant filter words
3. Take the spotlight off speech tags
4. Pick up dropped viewpoint
5. Trim anatomy-based action
6. Turn intention into action
1. Assess invasive adverbs
However, overuse is often a symptom of an author telling us what’s already been shown, which means the adverbs are repetitive and cluttering. In the two examples that follow, they can be ditched because 'fidgeted' shows the nervousness, and the apology in the dialogue shows the regret.
- Jane fidgeted nervously with the napkin.
- ‘I’m so sorry to keep you waiting,’ she said with regret. ‘It’s been one of those days.’
- Jane fidgeted with the napkin.
- ‘I’m so sorry to keep you waiting,’ she said. ‘It’s been one of those days.’
Even when adverbs are telling us something new, consider elegant recasts that use stronger verbs but still keep readers in the moment.
- Jane turned around suddenly and ducked.
- Jane opened the shed door cautiously and peeked in.
- Jane spun around and ducked.
- Jane inched open the shed door and peeked in.
2. Remove redundant filter words
The reader is already experiencing the story through a viewpoint character. For that reason, we often don’t need to be told that they realize, see, think or feel anything. We’re already in their heads.
It’s telling what’s already been shown.
- Jane’s phone trilled. She glanced at the screen and saw that it was James calling again.
- Matthew felt a thumping in his temples and thought about how that third glass of wine had been a bad idea.
- Jane’s phone trilled. She glanced at the screen. James again.
- Mathew’s temples thumped. That third glass of wine had been a bad idea.
Filtering pulls us out of the deep, limited viewpoint. Worse, it’s repetitive and obvious. Jane has already looked at the screen so we know her eyes are doing the work; telling us that she saw as a result of her glancing is redundant.
In the example where Matthew’s the narrative viewpoint character, we needn’t be told he feels the thumping in his temples, since if he weren’t feeling it he couldn’t report it. Nor do we need to know he’s thinking about that third glass because we’re already in his head.
3. Take the spotlight off speech tags
Sometimes tags aren’t even necessary because it’s obvious who’s speaking. Other times, we can replace a tag with an action beat than conveys movement and emotion.
Readers should be focused on the dialogue. If a showy tag is necessary to convey a character’s voice or mood, the speech might need a rethink.
In the examples below, the speech tags do the following:
- tell what the punctuation’s already shown
- tell what the dialogue’s already shown
- tell us what the dialogue could have shown but doesn’t
- express non-speech-related behaviour
- 'That’s extraordinary!’ Jane exclaimed, and ran her index finger over the polished wood.
- ‘Put the damn thing down now. That’s an order, soldier,’ Reja commanded, raising her rifle.
- ‘Stop,’ Mathew pleaded.
- ‘I really need to hit the sack,’ James yawned.
ALTERNATIVES
- ‘That’s extraordinary!’ Jane ran her index finger over the polished wood.
- ‘Put the damn thing down now.’ Reja raised her rifle. ‘That’s an order, soldier.’
- ‘Stop,’ Mathew said. ‘I’m bloody begging you.’
- James yawned. ‘I really need to hit the sack.’
4. Pick up dropped viewpoint
- The viewpoint character reports what they can’t know.
- The reader is given access to non-viewpoint characters' internal experiences.
The viewpoint character reports what they can’t know
Reporting what can’t be known often comes with filter phrases such as 'could tell (that)' and 'knew (that)'.
In this example, John is the viewpoint character. We experience the story though his senses.
There, behind the desk, sat Reja, the girl he’d dated two decades earlier.
‘Sergeant John Davis,’ he said, and held out his hand. He could tell she didn’t remember him.
Actually he can’t tell any such thing. It might seem that way, but for all John knows, she could be hiding it because she has another agenda. Telling us that’s not the case removes any underlying suspense – stops us asking the question.
This might seem like a small slip but it’s the kind of thing that turns over all the power of a limited/deep viewpoint to an all-knowing narrator and rips apart the tight psychic distance between reader and the viewpoint character.
Here are two recasts that avoid the viewpoint drop:
There, behind the desk, sat Reja, the girl he’d dated two decades earlier.
‘Sergeant John Davis,’ he said, and held out his hand.
She showed no sign of recognizing him.
There, behind the desk, sat Reja, the girl he’d dated two decades earlier.
‘Sergeant John Davis,’ he said, and held out his hand.
There was no recognition on her face.
Non-viewpoint characters’ internal experiences
Here we’re talking about head-hopping. It’s when readers are able to access emotions, mood and thoughts of a non-viewpoint character. In the example that follows, Reja is the viewpoint character.
Bloody fool. Who did he think he was? Reja jammed her hat down over her ears. No way was she leaving with him.
John could have kicked himself. He shouldn’t have come on that strong. Not after what she’d been through.
The solution is to recast the text so that these emotions, mood and thoughts can be inferred or accessed externally – for example, through movement or speech – by the viewpoint character only. Here’s a possible recast.
Bloody fool. Who did he think he was? Reja jammed her hat down over her ears. No way was she leaving with him.
John palmed his forehead and spluttered an apology. ‘I shouldn’t have asked. Not after … well, you know.’
5. Trim anatomy-based action
In the example below, we might remove the obvious body parts and focus more specifically on the part of John's legs doing the kicking and the impact of his action. As for the gun-toter, the hands have been ditched.
John kicked out with his legs. The woman stumbled, righted herself and came at him again, pistol raised in her hands.
ALTERNATIVE
John kicked out, slamming his heel into her kneecap. The woman stumbled, righted herself and came at him again, pistol raised.
6. Turn intention into action
Jane squeezed the detergent into the porridge. Just a couple of squirts to give Alice a taste of her own medicine.
However, when an author means to show the how of an action but tells of intention to act, there’s a problem. The red flag to watch out for is 'to'.
We can check whether the focus is on point by asking a question: What action do we want to show the reader (via Jane)?
If we want to show the reader that Jane can lift her wrist – because that’s what the first example below is showing us – we can leave as is.
However, that's rather dull; it's more likely that we want to show that Jane is checking the time, and so a leaner alternative is more effective.
Jane lifted her wrist to look at her watch. Bang on two.
ALTERNATIVE
Jane checked her wristwatch. Bang on two.
Summing up
And don't worry about them at first-draft stage. Use that space to get the words on the page. Put your sentence-level editing craft in play with a later draft, and once your story's structure, plot and characterization have been fully developed.
Further reading
- Author resource library (includes links to free webinars)
- Editing Fiction at Sentence Level: A Guide for Beginner and Developing Writers
- Making Sense of Point of View: Transform Your Fiction 1
- Making Sense of Punctuation: Transform Your Fiction 2
- ‘Playing with sentence length in crime fiction. Is it time to trim the fat?’
- ‘Playing with the rhythm of fiction: commas and conjunctions’
- ‘What is anaphora and how can you use it in fiction writing?’
- '2 ways to write about physical pain'
- 'What is head-hopping, and is it spoiling your fiction writing?'
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
FIND OUT MORE
> Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
> Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
> Learn: Books and courses
> Discover: Resources for authors and editors
Common examples are:
- there are/is/was/were
- it is/was
Take a look at the following pair. The first sentence is introduced by an expletive.
- There was a car parked outside the house.
- A car was parked outside the house.
When used well, expletives are enrichment tools that allow an author to play with a narrative voice’s register and the rhythm of sentences.
When prose is overloaded with them, it can feel cluttered with filler words that add nothing but ink on the page. At best, they widen the narrative distance between the reader and the POV character; at worst, they flatten a sentence and destroy suspense and tension.
Too much telling of what there is or was can rip the immediacy from a scene and encourage skimming. That’s a problem – it means the reader isn’t engaged and risks missing something.
Furthermore, if they’re not performing their rhythmic or emphasis role, expletives make sentence navigation more difficult because all they're doing is cluttering the prose.
Here's an example. Think I've overworked it? There are published books from mainstream presses with passages just like this made-up one.
It was a tiny room. There was a light switch with rust-coloured smudged fingermarks on the melamine surface. Was that blood? There was a noise coming from beyond on the back wall. It was a high-pitched whimper. Then there was silence. She held her breath and tiptoed forward.
Suddenly there was a scream.
The problem with the expletives in the passage above is that readers are bogged down in what there was rather than the viewpoint character's experience of discovery. Let's revise it to fix the problem.
The room was tiny. Rust-coloured fingermarks smudged the melamine surface of the light switch. Blood maybe. A noise came from beyond a door on the back wall. A high-pitched whimper. Then nothing. She held her breath and tiptoed forward.
A scream shattered the silence.
Notice how the narrative distance has been reduced in the revised passage. Now it's as if we're in the viewpoint character's head, moving with her second by second. We can focus on the room, the dried-blood fingermarks, the whimper, and the scream rather than the being of those things – their was-ness.
Removing the expletives and swapping in stronger verbs (smudged, shattered) enables us to tighten up the prose and introduce immediacy. And now there's no need for the told 'suddenly' – we experience the suddenness through the in-the-moment shattering.
As is always the case, obliterating expletives from a novel would be inappropriate because sometimes they're the perfect tool to help out with rhythm and emphasis.
The opening paragraph of Charles Dickens’s A Tale of Two Cities (p. 1) uses expletives galore, and masterfully at that. The repetition (anaphora) brings a steady rhythm to the passage that ensures the reader gives equal weight to the contrasting extremes – from best and worst to hope and despair.
The expletives introduce a detached sense of reportage that forces us forward rather than allowing us to dwell on any of the heavens or hells on offer. It’s simultaneously mundane and monstrous, and that's why it's magical.
And here’s an example from Dog Tags (p. 1) where omission of the expletive would rip the energy from the opening first line of the chapter and interfere with our understanding of which words we’re supposed to emphasize.
That was the USA Today headline on a piece that ran about me a couple of months ago.
Summing up
Grammatical expletives are a normal part of language and have every right to be in a novel. Overloading can destroy tension and make for a laboured narrative, but a purposeful peppering can amplify character emotion, moderate rhythm, and make space for the introduction of big themes in small spaces without sensory clutter.
Cited works and further reading
- Author resource library (includes links to free webinars)
- A Tale of Two Cities, Charles Dickens, W. W. Norton & Company; Critical edition, 2020
- Dog Tags, David Rosenfelt, Grand Central Publishing, Reprint edition, 2011
- Editing Fiction at Sentence Level: A Guide for Beginner and Developing Writers
- Making Sense of Punctuation: Transform Your Fiction 2
- ‘Playing with sentence length in crime fiction. Is it time to trim the fat?’
- ‘Playing with the rhythm of fiction: commas and conjunctions’
- 'Should I use a comma before coordinating conjunctions and independent clauses in fiction?'
- ‘What is anaphora and how can you use it in fiction writing?’
- 'Why "suddenly" can spoil your crime fiction'
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
Visit her business website at Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader, say hello on Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, connect via Facebook and LinkedIn, and check out her books and courses.
Reflexive pronouns can act as double tells by stating the obvious, and mar pace and tension.
Stating the obvious
- Max grabbed a fistful of dandelion leaves and shoved them into his mouth. Needs garlic, he thought to himself.
- Jenny wondered to herself about the dream – it had been so real, as if she’d had full control. And yet …
When it comes to internal musings, authors can ditch the reflexive pronouns. Thoughts take place inside a person’s head and, by definition, are offered only for the thinker – unless there’s telepathy going on in the novel!
Moderating pace and reducing tension
- Max ducked, rolled himself over the floor and grabbed the Browning. Fired out two shots. Both hit home.
- Ali sprinted down the street and swung herself into the shadows.
These are high-tension scenes. Max is in a shoot-out; Ali’s escaping danger. Every word stretches out the sentence. And as the sentence length loosens, so does the tension.
Look what happens when we remove the pronouns:
- Max ducked, rolled over the floor and grabbed the Browning. Fired out two shots. Both hit home.
- Ali sprinted down the street and swung into the shadows.
The sentences shorten, the pace increases – and so does the tension.
We shouldn’t omit all -self pronouns. There are occasions when a sentence works better with them. Sometimes they’re essential.
Clarity
In some cases, the pronoun is necessary for clarity. The reader can’t be sure of what the verb’s object is without it. In the examples below, removing the pronouns could leave the reader with questions: Ashamed of what? A promise to whom? Stop what? Consider whom an expert?
- Ordinarily, she’d have been ashamed of herself, but there was no guilt – not this time.
- I made a promise to myself never again to lose my rag over something so inconsequential.
- He couldn’t stop himself; it took five minutes to demolish the chocolate egg.
- I consider myself an expert, and no one will convince me otherwise.
Emphasis
The pronoun can be used to emphasize the person being discussed. Omission would leave the sentence grammatically intact but change the mood and pacing. In this case, it’s a judgement call on the author’s part.
- Sarah told me so herself.
- The queen herself told me.
- John hadn’t been the only one having a hard time. I myself had been suffering from anxiety at the time.
Sense
Some sentences don’t make grammatical sense without a reflexive pronoun. Remove them and the writing leaves more than questions: it’s unreadable.
- She had to defend herself from that monster – no two ways about it.
- Cass doused themself in perfume.
- Why shouldn’t he call himself the King of Hearts? Who cares if it sounds daft? Daft is good.
- He dragged himself to the top of the stairs.
At the top of this post, I offered examples of how -self pronouns can reduce tension. There will be occasions when an author wants to do exactly that.
- I was trying to make a new life for myself. That’s all there was to it.
- I was trying to make a new life. That’s all there was to it.
There’s a more staccato feel to the second version above that might jar if the author’s seeking a contemplative mood.
Still, too much self-ing can make even a stress-free scene overly wordy so it’s always worth thinking about whether a leaner version would be more immersive and get the reader from A to B faster.
In the first version of the triplets that follow, the pronouns introduce a chilled-out sense of laissez-faire to the movement. In the second I’ve omitted them. And in the third, I’ve ditched the mundane movement and focused on the essential beat.
- He found himself a chair and sat down.
- He found a chair and sat down.
- He sat down.
- Maxie busied themself with the coffee machine and settled down to read the letter.
- Maxie made a coffee and settled down to read the letter.
- Maxie read the letter.
- She got herself up and called Mel.
- She got up and called Mel.
- She called Mel.
It’s always worth an author spending a little time on thinking about how much micromanagement of a scene is necessary.
Will the reader care about the chair discovery, or that Maxie had a hot drink while they were reading the letter, or that the protagonist was no longer on the sofa when she called Mel?
Perhaps. If that stuff’s central to driving the novel forward, to reflecting mood, to grounding the character in the environment, the pronoun and the stage direction might be necessary. If it’s clutter that can be removed without damaging reader engagement, lean up the scene!
Summing up
Use reflexive pronouns when they’re necessary for clarity, sense and emphasis. Otherwise, consider leaner prose that focuses on what the reader needs to know to move forward in the story.
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
Visit her business website at Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader, say hello on Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, connect via Facebook and LinkedIn, and check out her books and courses.
Contractions are a normal part of speech. They help us communicate faster and improve the flow of a sentence.
Watch the following videos and listen to the spoken words. They feature people with very different backgrounds, sharing different stories, and in situations that demand varying levels of formality.
- A philosopher presenting a TED Talk about why the universe exists
- A fictional lawyer questioning a witness
- A child reading a poem
- A drug dealer describing his criminal activity
- A reporter’s voiceover on a news programme
- A vicar giving a sermon in a UK church
- A queen broadcasting a message to the nation
The people talking have one thing in common: they use contractions when they speak ... most (though not all) of the time.
That’s why when we want to write natural dialogue – dialogue that flows with the ease of real-life speech – contractions work.
How contractions affect the flow of dialogue
Take a look at this excerpt from No Dominion by Louise Welsh (Kindle edition, John Murray, 2017).
Here’s the contraction-free recast. It reads awkwardly, and leaves us unconvinced that what’s in our mind’s ear bears any relation to what we would have heard had this been real speech. And that means we’re questioning the authenticity of the story rather than immersing ourselves in it.
Contractions and genre
Some authors avoid contractions because of the genre they’re writing in. You’re more likely to see this in historical fiction than contemporary commercial fiction but it’s not strictly genre-specific and is more an issue of authorial style.
Here’s an excerpt from a contemporary psychological mystery, The Wych Elm (Penguin, 2019, p. 71). Tana French uses contractions in the narrative and dialogue. The speech sounds natural; the narrative that frames it is informal.
Compare this with Our Mutual Friend (Wordsworth Editions, 1997, p. 235). Dickens, writing literary fiction in the 1860s, still uses contractions in dialogue, although he avoids them in his more formal but wickedly tart narrative.
|
‘We’ll bring him in,’ says Lady Tippins, sportively waving her green fan. ‘Veneering for ever!’
‘We’ll bring him in!’ says Twemlow. ‘We’ll bring him in!’ say Boots and Brewer. Strictly speaking, it would be hard to show cause why they should not bring him in, Pocket-Breaches having closed its little bargain, and there being no opposition. However, it is agreed that they must ‘work’ to the last, and that, if they did not work, something indefinite would happen. It is likewise agreed they are all so exhausted with the work behind them, and need to be so fortified for the work before them, as to require peculiar strengthening from Veneering’s cellar. |
Now look at Ambrose Parry’s The Way of All Flesh (Canongate Books, 2018). The authors (Parry is the pseudonym used by Chris Brookmyre and Marisa Haetzman) don’t avoid contractions completely but the sparing usage does give the dialogue a more archaic feel. Here’s an excerpt from p. 259.
I doubt anyone would be surprised when I say that the setting is 1847. And so it works. However, if the novel were set in 2019, there’d be a problem. We’d consider those characters unrealistically pompous and the dialogue overblown.
Contractions, pace and voice
The decision to use or avoid contractions is a tool that authors can use to deepen character voice.
Specific contracted forms might enable readers to imagine regional accents, social status and personality traits such as pomposity.
P.G. Wodehouse is a master of dialogue. Bertie Wooster is a wealthy young idler from the 1920s. Jeeves is his savvy valet. The dialogue between the two pops off the page and Wodehouse uses or avoids contractions to make the characters’ voices distinct.
- Jeeves’s speech is often uncontracted. This moderates the pace of the dialogue and helps to render his voice as serious, formal, patient and long-suffering.
- Bertie’s speech is often contracted. This accelerates the dialogue and helps to render his voice as flighty, foolish and careless.
You can see it in action in The Inimitable Jeeves (Kindle version, Aegitus, 2019).
|
‘Mr Little tells me that when he came to the big scene in Only a Factory Girl, his uncle gulped like a stricken bull-pup.’
‘Indeed, sir?’ ‘Where Lord Claude takes the girl in his arms, you know, and says—’ ‘I am familiar with the passage, sir. It is distinctly moving. It was a great favourite of my aunt’s.’ ‘I think we’re on the right track.’ ‘It would seem so, sir.’ ‘In fact, this looks like being another of your successes. I’ve always said, and I always shall say, that for sheer brains, Jeeves, you stand alone. All the other great thinkers of the age are simply in the crowd, watching you go by.’ ‘Thank you very much, sir. I endeavour to give satisfaction.’ |
In Oliver Twist (Wordsworth Classics, 1992, p. 8), Dickens contracts is not (ain’t) and them (’em) to indicate the low social standing of Mrs Mann, who runs a workhouse into which orphaned children are farmed.
|
‘Why, it’s what I’m obliged to keep a little of in the house, to put into the blessed infants’ Daffy, when they ain’t well, Mr Bumble,’ replied Mrs Mann as she opened a corner cupboard, and took down a bottle and glass. ‘I’ll not deceive you, Mr B. It’s gin.’
‘Do you give the children Daffy, Mrs Mann?’ inquired Bumble, following with his eyes the interesting process of mixing. ‘Ah, bless ’em, that I do, dear as it is,’ replied the nurse. ‘I couldn’t see ’em suffer before my very eyes, you know, sir.’ |
Contractions and their impact on stress and tone
You can use or omit contractions in order to force where the stress falls in a sentence.
Compare the following:
- ‘I can’t believe you said that,’ Louise said.
- ‘I cannot believe you said that,’ Louise said.
By not using a contraction in the second example, the stress on ‘cannot’ is harder. The change is subtle but evident. With can’t the mood is one of disbelief tempered with a whining tone; with cannot the disbelief remains but the tone is angry.
Here’s another excerpt from The Way of All Flesh (p. 140). The speaker is a surgeon, Dr Ziegler.
|
‘I believe it is important to provide the best possible care for the patients regardless of the manner in which they got themselves into their present predicament,’ Ziegler continued. ‘Desperate people are often driven to do desperate things. I have known young women to take their own lives because they could not face the consequences of being with child; and some because they could not face their families discovering it.’
|
Parry’s dialogue doesn’t just evoke a historical setting. The style of the speech affects the tone too. The voice is compassionate, the mood stoic. However, the lack of contractions renders the tone precise and careful.
On p. 142, Raven – a medical student turned sleuth – talks with the matron about medical charlatanry:
- ‘Aye, though there is worse,’ said Mrs Stevenson.
Using there is forces the stress on is, and in consequence the tone is resigned. With there’s the stress would have fallen on worse, and we might have assumed a more conspiratorial tone, as if she were about to divulge a secret.
Contractions and narration style
If you’re wondering whether to reserve your contractions for dialogue only, consider who the narrator is.
Let’s revisit Tana French (p. 1). The viewpoint character is a privileged man called Toby, the setting contemporary Dublin. What’s key here is that the narration viewpoint style is first person.
It is Toby who reports the events of the mystery; the narrative voice belongs to him. His narration register is therefore the same as his dialogue register – relaxed, colloquial – and the author, accordingly, retains the contractions in the narrative.
For sections written in third-person limited, the narrative voice would likely mirror the viewpoint character’s style of speaking. However, if you shift to a third-person objective viewpoint, where the distance between the characters and the readers is greater, the narrative might handle contractions differently to dialogue. It's a style choice you'll have to make.
Guidance from Chicago
Still a little nervous? Here’s some sensible advice from The Chicago Manual of Style, section 5.105:
Evaluate the sound
Here are three ways to help you evaluate the effectiveness of contracted or contracted-free dialogue:
1. Read the dialogue aloud: Is it difficult or awkward to say it? Does it sound unnatural to your ear? Do you stumble? Does it feel laboured, like you’re forcing the flow? If so, recast it with contractions. If the revised version is smoother, and the integrity of the setting is retained, go with the contracted forms.
2. Ask someone else to read the dialogue: Objectivity is almost impossible when it comes to our own writing. If the plan is that no one but you will ever read your book, write your dialogue the way you want to write it and leave it at that. If, however, you’re writing for readers too, and want to give them the best experience possible, fresh eyes (and ears) will serve you well.
You could even give your readers two versions of the dialogue sample – one with contractions and one without – and ask them which flows better and reads most naturally.
3. Head for YouTube: Dig out examples of speech by people whose backgrounds, environments and historical settings are similar to those of your characters. Watching characters in action will give you confidence to place on the page what can be heard from the mouths of those on the screen.
Summing up
Whether to use contractions or not in dialogue is a style choice. There are no rules. However, a style choice that renders dialogue stilted and unrealistic is not good dialogue.
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
Visit her business website at Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader, say hello on Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, connect via Facebook and LinkedIn, and check out her books and courses.
The impact of ‘before’ and ‘after’ in fiction writing: Tacit and explicit chronology of action
17/2/2020
Here’s what to look out for and how to fix the problem.
Why writers include ‘before’ and ‘after’
The inclusion of ‘before’ and ‘after’ to tell the order of play is not an indication of poor grammar – not at all. There’s nothing grammatically wrong with these constructions.
It’s also why writers sometimes use several adjectives with similar meanings rather than one strong one, or an adverbial phrase to fortify a weak verb.
Some authors also fear that their writing will come across as too ‘plain’ or ‘simple’. Chronological nudges are an attempt to ornament the prose.
Tacit chronology of action
The things that we do occur in a sequence; they have a chronology. This is as much the case in real life as it is on the screen, in an audiobook and in the pages of a novel. That chronology is tacit – we don’t need to explain it because it’s understood.
Take a look at this excerpt from The Devil’s Dice by Roz Watkins (p. 79, HQ, 2019):
Watkins doesn’t tell us explicitly that the shuddering occurred before the laptop was put down, or that the laptop was moved before the character shifted the cat onto their knee. And yet we know. The sequence of events is implied by the order in which she places each clause. It’s tacit.
- First thing that happens: shudders
- Next thing that happens: moves laptop
- Next thing that happens: manoeuvres cat
- Next thing that happens: leans
- Next thing that happens: inhales cat odour
And that’s the thing with strong line craft – it allows the reader to immerse themselves in the chronology of action by showing us, clause by clause, what’s transpiring, instead of tapping us on the shoulder and telling us.
Explicit chronology of action
Let’s recast the Watkins excerpt with some explicit taps on the shoulder:
I see this use of timeline nudges frequently in the fiction writing of less experienced authors, and it’s problematic when overused. Here’s why.
1. Some readers might feel patronized
Not every reader will notice the use of chronology nudges. But some will, and since no author wants to alienate a chunk of their readership, why push the story over a cliff when we can work out the sequence of events from the order of the words?
Telling readers that X was done before doing Y, or after doing Z, is akin to saying: ‘Hey, just in case you’re not clever enough, let me spell it out for you.’
It’s a dumbing-down that readers in the know won’t appreciate.
2. The inclusion is unnecessary
If you’re still not convinced, ask yourself whether the inclusion of ‘before’ or ‘after’ as timeline nudges is necessary. It often isn’t.
If a character’s shuddering occurs at the beginning of a sentence, the reader will assume that shuddering is what’s happening right now. If a new action follows that shuddering, the reader will assume that – just like in real life – the moment has passed and something else is happening in the new now of the novel.
3. The reader is focused on the wrong thing
When writers create immersive fiction, the reader feels as if they are in the moment – this is happening, now that, now the other.
‘Before’ and ‘after’ are distractions that focus the reader on when rather than what’s happening. The former is telling; the latter is showing.
4. There are more words than are necessary
Not enough words leaves readers hungry for clarity. Too many gives them indigestion. The artistry comes in the form of balance.
As long as the sequence of events can be understood by the reader, consider whether timeline nudges such as ‘before’ and ‘after’ are cluttering your prose.
Take a look at these pairs of narrative text, each of which has a shown tacit chronology and an alternative told explicit sequence. Which versions are more suspenseful? Which are most immediate? Which flow better when you read them out loud?
I’ve used examples from published fiction for the tacit versions, and taken a little artistic licence – altering them in ways their authors never intended – for the explicit chronologies.
In the original version, the ‘and’ between the initial breath and the walk into the kitchen is a fine example of the power of a conjunction. It’s almost invisible, which gives us the space to take that breath with the viewpoint character. And having taken it, we’re ready to go into the kitchen with them.
In the edited version, ‘before’ pulls us away from that moment. The tension has fallen out of the sentence.
|
The Dream Archipelago, Christopher Priest, Gollancz, 2009, p. 201
|
In the original version, it’s as if we’re in the room, watching the man as he smiles and leans back. There is space for that action to have its moment. Then he blows the smoke – that’s the new moment; we’ve left the other behind.
In the edited version, ‘after’ shoves us past the leaning back and smiling before we’ve had a chance to savour it. It’s already gone, even though we’re still reading about it.
|
Jurassic Park, Michael Crichton, Arrow, 2006, Prologue from Kindle edition
|
In the original version, Crichton shows us the action. Perhaps, like me, you can hear the chunter of the helicopter blades in the air. Who’s in this helicopter? Men in uniform. They jump out. What will happen next? We’re shown: they fling open the door. There’s a sense of order, of clandestine and militaristic precision.
In the edited version, ‘before’ saps the suspense from the final sentence. We’re focused on the timeline rather than the action.
Summing up
The table below summarizes the impact of tacit and explicit chronology on prose.
|
Tacit chronology
|
Explicit chronology
|
|
Embraces the logic of standard sentence structure
|
Assumes readers don’t understand the word order
|
|
Allows readers to be in the now of the novel
|
Pushes readers into an external time and space
|
|
Shows us the story as it unfolds
|
Tells us the timeline of movement
|
|
Trims the fat
|
Clutters the prose
|
And if you’re worried that your prose will be too plain, think again. Immersive writing allows the reader to decorate the story with their own imagination.
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
Unanswered questions at the end of chapters place us in a state of suspense. We’ll try to predict the answers based on the information we’ve been given.
We might be proved right. I thought so!
We might be proved wrong. I didn’t see that coming!
Either way, as long as there’s suspense, we’ll turn the page. Here are some ideas, with examples from published fiction, about how to do it, so that even predictable outcomes are structured line by line such that readers are itching with anticipation.
1. Wrap up the chapter in the middle of something interesting
There are two people in a bedroom. They’ve survived a harrowing encounter. And there’s oodles of sexual tension between them.
A less confident writer might wrap up the chapter as follows:
Mark pulled off his tie and began to undo the buttons on his shirt.
They made love, then ordered food and drink – two omelettes and fries and a bottle of champagne – and, after they’d eaten, and drunk, they made love again.
[CHAPTER ENDS]
The problem here is that the suspense dissipates. Mark begins to undress but we don’t bother to wonder what will happen next – whether he and the woman will have sex, or try to but be interrupted, or do the deed and grab some food. We don’t need to – we’re told.
Fear not! This is actually a tweaked version of an excerpt from Solo by William Boyd, Vintage, 2014 (pp. 259–60). Boyd is cannier. This is what it really looks like:
|
‘I’m sorry I shot you,’ she said, and slipped into the bed. ‘But I did it to save your life.’
Bond pulled off his tie and began to undo the buttons on his shirt. [CHAPTER ENDS] Bond and Blessing made love, then ordered food and drink – two omelettes and fries and a bottle of champagne – and, after they’d eaten, and drunk, they made love again. |
In the real version, we do ask those questions. The artistry lies in the fact that we have to turn the page to find the answers and relieve our suspense.
They’re given in the next chapter. A sex scene follows. It’s an interlude – a chance to breathe, for them and us – before Bond leaves and sets up a diversion that will confuse the CIA’s surveillance of him.
2. Wrap up the chapter with foreshadowing
Chapter endings that tell of incoming storms are powerful. When they’re short and taut, even better! Take a look at this super example from p. 210 of Clare Mackintosh’s Let Me Lie (Sphere, 2019):
|
I lean my back against the stained-glass panel. I wonder if she’ll knock and ring, as she did this morning. There’s a moment’s pause, then I hear her footsteps on the steps, on the gravel. Silence.
My mind whirs. My father was a violent man. So cruel to Mum that she faked her own death to escape him. And now he’s coming for me. [CHAPTER ENDS] |
That final line is like a punch in the gut. It begs us to ask: When will he come? What will he do? And how will she protect herself? It’s six words of masterful suspense.
3. Wrap up the chapter with emotional reflection
In the The Man with No Face by Peter May (Riverrun, 1981), the protagonist, a journalist called Neil Bannerman, walks into a restaurant and alerts a minister that he has evidence about a government cover-up. That’s the juicy bit.
Bannerman then exits, leaving the minister to mull over the revelation. That’s the mundane bit and May needs a way to close the chapter with a pop. Emotional reflection is the tool of choice.
Here’s the excerpt from p. 233:
|
Before stepping outside once more into the snow he glanced back towards the bar. Everyone in there knew something had passed between Bannerman and the Minister, though no one knew what. In the competitive world of newspapers, the cardinal sin was not knowing what the story was. None of those pressmen would enjoy their meal tonight. Nor would the Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs.
[CHAPTER ENDS] |
The journos and minister won’t be enjoying their meal but this isn’t an exercise in gastronomy. The end-of-chapter suspense comes in the form of questions: Will there be consequences for Bannerman? How will those play out? Will the minister get his just deserts?
4. Wrap up the chapter with a surprise interruption
Another way of wrapping up a chapter when the big stuff has already played out is to introduce some sort of surprise interruption. Perhaps there’s a knock on the door from an unexpected visitor, or an odour that forces the viewpoint character to direct their attention elsewhere.
Here’s another excerpt from Let Me Lie (p. 226). Murray, the viewpoint character, has just had a telephone call with Anna, during which he told her that her parents had indeed been murdered. She becomes emotional and commands him to drop the investigation, despite her bringing the case to him in the first place.
What would ordinarily be a domestic mundanity serves to show his mood; his shock is so immersive that he’s forgotten everything around him until the alarm goes off.
We leave the chapter imagining the shrill noise, the odour of burnt food, the smoke in the kitchen, and wondering what on earth has happened to make Anna change her mind.
5. Wrap up the chapter with a shocking last line
There’s nothing better than a final line that the reader doesn’t see coming. Here’s a magnificent example from David Baldacci’s True Blue (Kindle edition, Macmillan, 2009).
In Chapter 4, we meet Roy, a young lawyer. He finishes a game of basketball and slopes back to the office where, we learn, he earns a healthy pay cheque by plea-bargaining on behalf of mostly guilty defendants.
|
After getting some work lined up for his secretary when she came in, he needed some coffee. It was right at eight o’clock as he walked down the hall to the kitchen and opened the refrigerator. The kitchen staff kept the coffee in there so it would stay fresher longer.
Roy didn’t get the coffee. Instead he caught the woman’s body as it tumbled out of the fridge. [CHAPTER ENDS] |
Baldacci sets up the whole chapter as just another day at the office. We should know better than to be lulled into this false sense of security, but Baldacci’s narrative is strong enough from the start to convince us this might go in another direction.
Maybe Roy is crooked. Perhaps he’s about to be fired. Maybe he’s going to get a phone call telling him he has to go to court and represent someone he’d rather not. What we don’t expect is the wallop when a body falls out of the fridge.
And now we have a ton of suspenseful questions. Who is she? How did she get in the fridge? Why was she killed? To find out, we’ll have to turn the page.
6. Wrap up the chapter with dialogue that demands answers
One great line of dialogue can close a chapter beautifully. No action beats, no narrative, no response – just the spoken word. It works as an outro when the speech leaves us with questions, and therefore in suspense.
Here's an example from New Tricks by David Rosenfelt (2009, Grand Central Publishing, pp. 215–16):
The dialogue forces us to wonder: Why has Richard not carried out the redirect? Has some new evidence come to light? How will this affect the case?
Rosenfelt doesn’t dampen the suspense by cluttering his prose with the detail of what came next – maybe people in the courtroom looked surprised or confused; perhaps there was an objection, and the judge banged their gavel and announced a recess.
Instead, all that stuff is left unwritten – we just imagine it. It’s one line of dialogue and the chapter’s done.
7. Wrap up the chapter in the middle of one character’s speech
Here’s Rosenfelt again in Dog Tags (Grand Central Publishing, 2010, pp. 28–9). Unlike in the example above where there’s a natural chapter break because of a shift from the courtroom to the chambers, this time he inserts the chapter break in the middle of one person’s speech.
Less experienced authors might shy away from this, but it can work – if it’s an appropriate suspense point that leaves the reader reeling with questions.
|
“He wants me to take his dog?” I ask, my relief probably showing through. Willie and I have already placed hundreds of dogs through our foundation, and adding one is no hardship at all.
“No. He wants you to defend his dog.” “From what?” “The government.” [CHAPTER ENDS] “He’s like a celebrity here, Andy.” Fred Brandenbeger is talking about Milo, who has been placed in the Passaic County Animal Shelter. |
That final line is a shock, for lawyer Andy Carpenter and us. Why would a dog need a lawyer? How can such an absurd conversation be happening? We learn the answers to these questions in the next chapter, and that’s exactly where they should be because ‘The government’ is the suspense point that grabs us by the scruff of the neck and demands we keep reading.
Do you know when it’s closing time?
Like artists who can’t put down a paintbrush, less confident writers sometimes lack the courage to end with one line that evokes questions rather than solutions.
Yet that’s what the authors in all the examples above have done, and that’s why their outros are suspenseful and page-turning.
If your chapters have a saggy bottom, maybe you haven’t identified closing time. I line edit for an author who writes knockout chapter endings … he just places them 10 lines further up the page than they should be to create a suspenseful finale!
When you find yourself stuck, look up the page to find the point that will make the reader think How’s that going to play out? or Why did she do that? or That was a surprise! or Ha! You deserved that. … those few lines that will kick them up the backside and push them forward.
If those lines are already there, think about whether they should be moved to the end of the chapter, or whether the prose after them should be shifted (or even deleted).
If they’re not there, write them.
Think about the very last sentence in your chapter too. How long is it? Your writing style and genre might dictate the style of your final lines but notice how lean the word count is in most of the examples above. The brevity acts like a command: Read me. Pay attention. Turn the page.
Summing up
Every chapter should end with a pop, regardless of genre. Those last few lines are what the reader remembers before they pause. An otherwise beautifully crafted chapter can be ruined if it flops at the finishing line.
Find the suspense point – the lines that make readers ask questions – and use them to wrap up your chapter. And pay attention to the very last sentence. Sometimes less is more.
Related resources
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
Narrative distance and the layers of reader experience
The closer the reader feels to what’s being narrated, the more immersive the experience.
It can help to think in terms of how many layers readers must travel through to experience the story through a viewpoint character’s lens.
Let’s imagine Joe, a young teen. His journey is unveiled via a third-person past-tense narrator.
The viewpoint style is limited, or close – we can access what Joe can hear, see, smell, touch, feel (his emotions) and think. That accessible information can be either be shown or told.
With each approach, the reader pushes through various layers of the story as they are experienced by Joe.
Joe heard the sounds of grunts coming from his mother’s bedroom. He pushed the door open and looked on in shock as his mother screeched and pulled the duvet over herself and their neighbour Mr Michelson.
He looked at the bed and saw them both lying there naked. She started talking fast but he couldn’t make out what she was saying because everything felt confused in his head. He wondered where Dad was, and felt worried about Christmas and the trip to Grandma’s. And what about soccer practice with Mr Michelson’s son, Justin? he thought. Then he remembered how Abbie’s parents had got divorced, and how awful she’d said it had been.
EXAMPLE: A SHOWN NARRATIVE
The grunts were coming from his mother’s bedroom. Joe pushed the door open. His mother screeched and pulled the duvet over herself and--
And their neighbour Mr Michelson.
They were both lying there naked and she started talking fast but the words made no sense – just a wah-wah-wah like Charlie Brown’s teacher in those old TV shows. And where was Dad, and what about Christmas and the trip to Grandma’s and soccer practice with Justin, Mr Michelson’s son, for Christ’s sake? And then there was what happened to Abbie. Her parents had got divorced – a right old bloody stink-up, she’d called it.
Gridding the layers
Layers of doing being done: Putting the reader on pause
Instead of seeing a bed (and doing it with Joe because he’s the viewpoint character), we see Joe seeing a bed. We’re not focused first and foremost on the bed, but on Joe doing seeing.
That extra layer increases narrative distance, unless that’s the effect you want to achieve, because it’s like a tap on the shoulder, telling us what to do. It screams: Reader, you’re not in this world; you’re just holding a book.
Limited narrative viewpoint and the reader
- that when there’s an odour, it’s being smelled
- that when there’s an object in front of a sighted character’s eyes, it’s being seen
- that when they’re processing internal questions and ideas, there’s thinking being done
- and that when emotion is in play, our character is feeling it.
Shown narratives respect this – it’s storytelling. Told narratives overplay it – it’s storytelling-telling!
If you think you might be storytelling-telling, try gridding a section of narrative to identify each layer. Then recast to tighten up the prose. Chances are, it’ll be more immediate and immersive.
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
Visit her business website at Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader, say hello on Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, connect via Facebook and LinkedIn, and check out her books and courses.
- Flatness: Tension and dynamism are reduced
- Woolliness: The narrative voice can’t make its mind up
- Distance: The reader is pulled away from the story
Authors sometimes introduce tentative language into a novel because:
- They’re afraid of dropping viewpoint
- Their narrative voice lacks confidence
- They think it’s appropriate
Tentative language: words to watch out for
I’m not suggesting you remove every tentative word; some might be deliberate and necessary. More likely, you’ll be checking that your prose isn’t rife with them.
Still, these little blighters can slip in accidentally and it’s worth taking the time to root them out and decide whether to give them space on your page or remove them.
Here are some of the words (or word groups) to watch out for:
- as if to
- almost as if
- appeared to
- considered
- could
- hoped
- looked as if/looked like
- maybe
- might
- perhaps
- presumably
- probably
- seemed
- thought
- wondered
When there’s a problem, it can sometimes be fixed with a simple deletion, or a stronger verb.
When viewpoint, tension and reader immersion are at stake, more intervention might be required.
How to fix it without dropping viewpoint
I see the likes of seemed, appeared, and looked as if creeping frequently into line editing projects for less experienced authors because they want to hold viewpoint.
Hats off to them – I’ll take a seemed over a head-hop any day of the week! Still, there might be a better fix.
Here’s a framework you can use to recast in a way that removes the uncertainty but keeps the narrative alive.
|
Fixing framework that holds viewpoint
|
|
Luke peeked around the headstone. The hooded man seemed frustrated.
The sentence is flat though. Yes, we readers are still in Luke’s head but it’s not a particularly interesting space. There’s no tension in our observations from his hiding place.
Here’s how the fixing framework helped me recast in a way that shows readers the hooded man’s assumed frustration, as seen by Luke:
Luke peeked around the headstone. The hooded man glanced at his watch and swore under his breath. His foot lashed out, knocking over a grave vase. The stagnant water stunk and Luke wrinkled his nose.
Thom turned and tripped over the blind guy’s white stick – Mikey, someone had called him. He looked at Mikey, who seemed almost to be picking out Thom’s facial features in his mind.
But there’s a problem. If Mikey were the viewpoint character, his imagining Thom’s face would make for an interesting narrative. However, it’s Thom’s head we’re in. In this case, the assumption seems off, too big to believe.
When I listen to someone speaking, I tend to use my eyes to focus on their mouths; my friend with restricted vision tends to move his head so that his ears are more in play. Sighted people in his company need to be aware that his eyes don’t focus directly on a speaker even though he’s fully engaged.
If we place this experience within the fixing framework, we can imagine Mikey’s physicality and the effect on Thom, the viewpoint character.
Thom turned and tripped over the blind guy’s white stick – Mikey, someone had called him. Mikey tilted his head, gaze off-centre, ear trained on Thom’s blustered apology.
How to fix an insecure narrative voice
In the examples below, the tentative words have crept in because the authors are still developing the confidence to make every word count.
Useful tools of the trade include deletion, stronger verbs, smoother recasts, and free indirect style.
The fixes below are suggestions only, offered so you have an idea of what to look out for and how you might tackle the solution. The approach you use will depend on your writing style and the mood of the scene.
When tentative language creates a flat sentence
In these examples, the tentative mood is justified but the sentences are rather flat. We need to inject tension.
|
Original
|
Tamsin Johns came to mind. He wondered what her story was.
|
|
Free indirect style
|
Tamsin Johns came to mind. What the hell was her story?
|
|
Original
|
Confused, Ava wondered if he’d thought she was going to rob him.
|
|
Recast
|
Ava shook her head. It was odd, like the guy had thought she was going to rob him.
|
|
Original
|
Arty thought the new door seemed not to fit the others in the old house.
|
|
Recast
|
Arty touched the cherrywood door. It was different to the others, the grain fine and straight, the lacquer smooth under his fingertips.
|
In these examples, the tentative words relate to viewpoint characters’ experiences. The uncertainty introduces distance because it pulls the reader out of their experience. It makes us say, ‘Why the lack of commitment? Doesn’t the viewpoint character know?’
Once more, I’ve used real examples and adapted them to disguise the originals.
|
Original
|
Her body appeared to hum with fear.
|
|
Deletion
|
Her body hummed with fear.
|
|
Original
|
Eleanor gasped as the craft shot into the air and was gone in what seemed like an instant.
|
|
Deletion
|
Eleanor gasped as the craft shot into the air and was gone in an instant.
|
|
Stronger verb
|
Eleanor gasped as the craft shot into the air and vanished.
|
|
Original
|
Debs scrolled through her contacts, found his name and hit DELETE. Hilary probably thought she could do better, and Debs agreed.
|
|
Deletion
|
Debs scrolled through her contacts, found his name and hit DELETE. Hilary had said she could do better, and Debs agreed.
|
In these examples, the tentative words work. They show the reader that the viewpoint character is guessing.
She glowered as if to say, You really think there’s enough meat on that plate?
Mark glanced at the blue car. There were two people inside, neither familiar. Might be undercover cops, but he legged it anyway … just in case.
Mark glanced at the blue car. There were two people inside, neither familiar. Might be undercover cops, but he legged it anyway … just in case.
A haze hung in the air – maybe brick dust from the fallen building or ash from the fire. It stung his eyes and irritated his throat.
The news knocked the breath out of her. Jamie had seemed happy the last time they’d met. Ecstatic even, what with the new job, the kayaking holiday, that girl he’d met the week before.
She combed the beach for Ben’s blue sun hat, pushing the unthinkable to the back of her mind. Thought it through. Probably with Mark at the rockpool. The café maybe. Or the groyne or the dunes. Her head spun left, right, left again.
Summing up
As soon as a writer or editor begins line editing fiction, subjectivity comes into play. It’s rare that there’s a right or a wrong way.
With that in mind, don’t ban tentative language in your prose; just watch out for it. It may well have the right to be there, though it shouldn’t trump tension or add clunk.
If removing it messes with viewpoint, use the fixing framework to craft an alternative shown narrative.
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
Good dialogue is the icing on the cake of a well-structured novel. Bad dialogue will mar a well-structured narrative and bury a story that is barely hanging in there. Before we look at what makes great dialogue, let’s look at what dialogue isn’t:
- It’s not everyday conversation – much of that is boring and has no place in a novel.
- It’s not a narrative – that tells us what’s happening in a story. Dialogue should show us how characters respond to those events.
- It’s not a tool to set up the next character’s lines – that’s a waste of words on the page. Every line should have a purpose, whoever’s speaking it. Every line should tell us something about the character – who they are, how they’re feeling and what they want.
- It’s not a backstory-delivery mechanism that the characters are already familiar with – that’s maid-and-butler dialogue and a misfire.
- It’s not a monologue – that’s best left for viewpoint characters mulling things over in their own time, unless your intention is to show one person being bored rigid by another. If only one person’s doing all the talking, ask yourself why the other person on the page is still in the room.
3 components of effective dialogue
‘Dialogue should be the character in action,’ says John Yorke in his must-read Into the Woods (p. 151). Yorke’s talking about the art of screenwriting but the advice is just as pertinent for novelists. I recommend you read it even if you have no intention of writing for the screen because it’s a masterclass in storytelling, whatever the medium.
When we stop thinking about dialogue as words spoken – as conversations – and instead frame it in terms of characters, we create something that’s fit for a novel.
What does your dialogue tell readers about who your characters are, how they’re feeling, and what their motivations are?
|
3 COMPONENTS OF EFFECTIVE DIALOGUE
|
- Character intent: How characters speak tells us what they want to do. Perhaps they’re asking questions for the purpose of discovery and understanding whodunit (doctors, lawyers, PIs and police officers regularly use dialogue in novels to this end), but dialogue can express a multitude of motivations. Ask yourself what your character wants every time they open their mouth.
Unreliable dialogue
What a character expresses through dialogue need not match their true voice, mood or intent. Unreliable dialogue is powerful precisely because it jars the reader by masking the truth (which the characters themselves may even have buried).
Imagine this scenario: John has been kidnapped by Jane. They met in a club where she spiked his drink. He started to feel unwell and she offered him a ride to the Tube station. He never made it. He’s been held captive for several days, during which time he’s been physically abused and deprived of food. He’s frightened out of his wits, and weak to boot.
The dialogue between John and Jane could go as follows: John raves and rants, telling Jane her behaviour is monstrous, that Jane’s going to pay for her actions and that he’s going straight to the police as soon as he’s escaped. Jane responds in fury, telling John he deserves it all and how there’s no way he’ll ever escape.
Or the dialogue could be unreliable. John might be polite, sycophantic even, as he thanks her for the water she provided, compliments her on her appearance, or asks her about her life. Through that speech, we are shown his desperation. It’s about keeping her on side and calm in order to save himself.
And Jane’s verbal response might be chipper, seductive even. Through that dialogue, we are shown her psychosis.
The result is a sinister verbal exchange that allows us to explore the inner workings of the characters’ minds without it being forced down our throats via an all-to-obvious narrative that’s centred around the viewpoint character.
Breaking free of viewpoint limitations
Most novelists opt to hold third- or first-person narrative viewpoints. That means the story in a chapter plays out through one person’s perspective.
When authors drop viewpoint, readers end up playing a game of narrative table tennis in which they bounce from one character’s head to another. We know who everyone is (voice), what everyone’s feeling (mood), and what everyone wants (intention) all of the time. Readers become disengaged because they don’t have time to immerse themselves in any one character’s experience.
Good dialogue allows writers and readers to break free without head-hopping. Through dialogue, readers can intuit the voice, mood and intention of multiple characters, yet the singular narrative viewpoint remains true throughout. That keeps the reader engaged and the writing taut.
Purposeful dialogue in action
Here’s an excerpt from Lee Child’s Never Go Back (pp. 457–8). I chose it because I’ve also seen the movie, which allowed me to compare my experience of the screen dialogue (and the advice Yorke gives) with the novel’s, and because there are no action beats, only two speech tags and no narrative. It’s just dialogue between a teenage girl and Jack Reacher.
Reacher said, ‘No you’re not in trouble. We’re just checking a couple of things. What’s your mom’s name?’
‘Is she in trouble?’
‘No one’s in trouble. Not on your street, anyway. This is about the other guy.’
‘Does he know my mom? Oh my God, is it us you’re watching? You’re waiting for him to come see my mom?’
‘One step at a time,’ Reacher said. ‘What’s your mom’s name? And, yes, I know about the Colt Python.’
‘My mom’s name is Candice Dayton.’
‘In that case I would like to meet her.’
‘Why? Is she a suspect?’
‘No, this would be personal.’
‘How could it be?’
‘I’m the guy they’re looking for. They think I know your mother.’
‘You?’
‘Yes, me.’
‘You don’t know my mother.’
‘They think face to face I might recognize her, or she might recognize me.’
‘She wouldn’t. And you wouldn’t.’
‘It’s hard to say for sure, without actually trying it.’
‘Trust me.’
‘I would like to.’
‘Mister, I can tell you quite categorically you don’t know my mom and she doesn’t know you.’
‘Because you never saw me before? We’re talking a number of years here, maybe back before you were born.’
‘How well are you supposed to have known her?’
‘Well enough that we might recognize each other.’
‘Then you didn’t know her.’
‘What do you mean?’
‘Why do you think I always eat in here?’
‘Because you like it?’
‘Because I get it for free. Because my mom works here. She’s right over there. She’s the blonde. You walked past her two times already and you didn’t bat an eye. And neither did she. You two never knew each other.’
WHAT WE LEARN
- Viewpoint: Reacher is the viewpoint character. However, through the dialogue, readers are able to access information about him and the teenager.
- Voice: Both characters speak in a no-nonsense fashion. Reacher might think he holds the balance of power, given his job and age, but the girl’s streetwise tone suggests she thinks otherwise; they’re equals.
- Mood: Reacher is calm (we’d expect nothing more) and measured, but there is emotional engagement; he seems keen not to give too much away (probably in respect of the fact that he’s talking to a child, perhaps his daughter). As for the girl, she’s almost disinterested. I imagine her stuffing fries into her mouth, as focused on her food as she is on the conversation ... until she thinks her mother might be in trouble. Child doesn’t tell us, but I can see her in my mind’s eye, mouth full, looking at him, just a twitch of alarm registering in her expression. There’s almost a sense of the traditional mother/daughter relationship reversed; this is a kid who’s used to looking after herself. There’s movement in this dialogue; the speech is infused with its own action beats.
- Intent: Reacher wants to find out who the mother is. This exchange is all about building trust with the girl in order to achieve that. The girl needs someone she can turn to because bad people are watching her and her mother. She wants to know how Reacher might know Candice; Reacher wants to keep the possible sexual encounter and his resulting paternity to himself. The girl’s not stupid and picks up on his vague inference to a sexual encounter. As the conversation and the chapter close, Reacher and the readers discover that Candice and our protagonist have never met, and that the girl can’t be his daughter.
This is characters in action, expressed through speech. Child makes every line count towards the chapter denouement. If he was tempted to introduce narrative and action beats that ensured we’d get it, it doesn’t show. In fact, they would have been interruptions and slowed the pace. Instead, he trusts us to do the work because the dialogue gives us everything we need.
Here’s an excerpt from The Poison Artist by Jonathan Moore (pp. 244–5). I chose this because of the contrast between Kennon and Emmeline’s speech.
This time, his voice wasn’t much more than a whisper.
[...]
“Inspector, you’ll hit somebody,” Emmeline said.
[...]
“You look sick, Inspector,” Emmeline said. “I could get you something to drink. A glass of water, maybe? Something a little stronger?”
Kennon fired again and Emmeline didn’t even flinch.
The bullet missed her by ten feet, punching a hole in the back of the building.
“Stop—”
“You should be more careful what you touch,” Emmeline said. “Some things can go right through the skin.”
WHAT WE LEARN
- Viewpoint: Even though Emmeline isn’t the viewpoint character, we get to access her transgressor headspace through the dialogue, and the result is powerful and sinister.
- Voice: Kennon doesn’t say much, but what he does say is what we’d expect from a trained inspector, though it’s offered quietly. Emmeline, however, is pathologically measured. We’re left in no doubt that she’s dangerous.
- Mood: We sense Kennon’s fear and desperation through his truncated, whispered speech. There’s almost exhaustion in play. Emmeline, in contrast, is seductive (offering him a drink as if she were hosting a dinner party). Given the torture in evidence, her dialogue is obscene.
- Intent: Kennon is trying to save himself, Caleb and the twitching man, but he’s playing by the rule of law, warning Emmeline that he will fire his gun. Emmeline wants to finish her game, and her desire to play is evident in her speech. Of course, this may be unreliable; it could be masking a deep-seated fear that she’ll be harmed or killed.
This, too, is characters in action, expressed through speech. Moore draws us deep into the transgressor’s mind – even though she’s not the viewpoint character. Her dialogue, juxtaposed with Kennon’s exhausted near-silence, generates a powerful scene that oozes with sickly tension.
Here’s a third example from Harlan Coben’s Run Away (pp. 68–9):
Ingrid wore a long thin coat. She dug her hands into her pockets. “Go on.”
“Aaron was mutilated.”
“How?”
“Do you really need the details?” he asked.
[...]
“According to Hester’s source, the killer slit Aaron’s throat, though she said that’s a tame way of putting it. The knife went deep into his neck. Almost took off his head. They sliced off three fingers. They also cut off ...”
“Pre- or post-mortem?” Ingrid asked in her physician tone.
“The amputations. Was he still alive for them?”
“I don’t know,” Simon said. “Does it matter?”
WHAT WE LEARN
- Viewpoint: Simon is the viewpoint character but through Ingrid’s speech we learn how she uses her professional mindset to manage stressful situations.
- Voice: Simon’s voice is emotional and verbose; Ingrid’s is precise and clinical.
- Mood: Simon’s disgust and distress are evident. You can almost feel the words falling out of his mouth. Ingrid’s speech exudes clinical detachment. She’s in doctor mode.
- Intent: Simon wants to unload. Ingrid wants to understand.
Again, through speech we see the characters in action. The contrasting voices and moods show us Simon and Ingrid’s different intentions. There’s no need for more than a peppering of supporting narrative.
Summing up
- Make your characters’ speech count. Use it to show who the character is (voice), how they feel (mood) and what they want (intention).
- Play with unreliable dialogue if it will enhance our understanding of characters’ emotions and motivations. Those deliberate juxtapositions will deepen our engagement.
- Realistic everyday speech, while authentic, is dull, invasive and will disengage your reader. Remove it!
Free dialogue enrichment tool
To help you think about your characters' voices, moods and intentions, and how these will enrich your dialogue, download this tool. It's a fillable PDF with ready-made examples and space for you to record your own decisions.
|
Cited sources
|
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
Visit her business website at Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader, say hello on Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, connect via Facebook and LinkedIn, and check out her books and courses.
Is one of your characters telling another something they already know just so you can let your reader access backstory? If so, you’ve written maid-and-butler dialogue. It’s a literary misfire and should be avoided.
Here's an extreme example:
‘Thanks. Yeah, I’m thrilled to bits, though there have been times when I’ve yearned for your nine-to-five job as an editor in a small fiction publishing company on the outskirts of Norwich.’
SOLUTIONS
- Dialogue should be purposeful. If you’re using it to introduce information, have the characters seek answers to questions they don’t know the answers to.
- Unveil backstory that’s known to the speakers through the narrator, not the speech:
Three years in fact. Clever Jen had notched up a first in archaeology from Nottingham Uni while I was inching my way up the publishing ladder with a small fiction press on the outskirts of Norwich.
‘Yup,’ she said. ‘Seems like an age. How’s tricks in the world of business? Found the next Booker Prize winner yet?’
Problem 2: Real but mundane
The conversations many of us have in real life are deathly boring. Here’s one I had recently:
‘Yes, please. Coffee please. Er, or tea. Um, whatever you’re having. As long as it’s wet and warm.’
‘I’m having coffee but I’m happy to make you tea.’
‘No, erm, coffee’s perfect. Thanks.’
‘Milk and sugar?’
‘Just milk. No sugar, thanks.’
‘Okay.’
‘Cheers.’
‘Um, can I use your bathroom?’
‘Of course you can. There’s extra loo roll in the cabinet if you need it.’
It’s realistic, certainly, but has no place in a novel. Most of the words are a waste of space, and the trees that were felled to create the paper on which they’re written deserve better.
Dialogue needs to be natural, but not too natural. The best dialogue is a hybrid of the real and the contrived, ‘a kind of stylised representation of speech’ as Nicola Morgan calls it in Write to be Published (p. 151).
SOLUTIONS
- No one in Star Trek ever goes to the loo. Viewers know that the crew members of the USS Enterprise need to use the bathroom and like their hot drinks served in a variety of ways. The writers know all of that’s best left to our imagination. The same applies in novels.
- Replace filler dialogue with narrative or speech that drives the novel forward.
- Minimize the stumbles. They’re natural and frequent in real life, but mar the flow of dialogue when overdone on the page.
Problem 3: Written accented dialogue
It can be tempting to convey accents with phonetic spellings, as in these appalling examples below:
‘Ve have vays of getting vat ve vant.’
There are so many problems with this approach that I recommend you avoid it altogether. Bear in mind that dialogue tells us what words have been spoken, not how they’re spelled.
Phonetic spelling can turn dialogue into pastiche, and offensive pastiche at that. It’s also difficult to absorb and distracts readers from your story.
SOLUTIONS
- If your novel is written in, for example, British English, use standard spelling regardless of how your character pronounces words.
- Use location rather than pronunciation to enrich characterization – how where they’re from affects the story, their perception of the conflict or their approach to solving it.
- Read ‘How to convey accents in fiction writing: Beyond phonetic spelling’ for more ideas on how to flavour characters’ voices.
Problem 4: Troublesome tags
The function of speech tags is to tell the reader who’s speaking. They shouldn’t push the dialogue into the background. Nor should they repeat what the reader knows from the dialogue.
Furthermore, the verbs we use to tag the dialogue should be speech-related. Otherwise we end up with a reality crash that jars the reader.
‘Come here. Let me show you how it works,’ demonstrated Jonathan.
‘I swear I’ll stick this knife where the sun doesn’t shine if you don’t give me the letter,’ brandished Marcus.
SOLUTIONS
- Said is often best. Readers are so used to seeing it that it’s almost invisible.
- Use action beats to indicate movement.
- Use emotionally evocative adverbs to modify the tag.
- Recast the dialogue so that a showy tag is unnecessary.
- Read ‘Dialogue tags and how to use them in fiction writing’ for more ideas on tagging artfully.
- Read ‘What are action beats and how can you use them in fiction writing?’
Problem 5: Talking heads and monologues
Some books can turn into podcasts on the page when dialogue isn’t grounded in the physical environment.
Too much dialogue can make the reader feel dissociated from the story, as if the characters are talking in the cloud.
In Jo Nesbo’s The Bat, McCormack starts talking on p. 249. On p. 250, Nesbo introduces one line of movement: ‘He turned from the window and faced Harry.’ Then McCormack’s off again. He doesn’t stop talking until p. 251.
It’s a monologue in which Hole, the viewpoint character, seems to be nothing more than a receptacle for McCormack’s ear bending. There’s a little bit of back and forth with Hole, plus some action beats in the lower third of p. 251, but then McCormack’s off again for all of p. 252 and the top third of p. 253.
The blue highlights show how much of these four pages are taken up with just one character’s speech.
SOLUTIONS
- Think about what’s physically surrounding your characters. What can they smell, see, hear? Where are they and what time of day is it?
- How are the characters moving as they talk? Are they fidgeting, escaping, hiding, snuggling?
- If your viewpoint character is on the listening end of a long rant, how are they feeling and moving? What are they seeing?
- Could some of the dialogue be recast as narrative?
- If you’re worried about slowing the pace, use action beats rather than longer narrative descriptions to break up the speech.
Problem 6: ‘Too many vocatives, Louise.’
The vocative case enables the writer to indicate who’s being spoken to in dialogue. In a bid to avoid speech tagging, some less experienced writers overuse vocatives, which renders the speech unnatural.
Next time you get the opportunity to listen to a conversation between two people, notice how often they use each other’s names. You might find they don’t, other than for emphasis.
Overuse can labour dialogue, as this example illustrates:
‘I didn’t murder anyone, Johnny. And I’m gutted that you felt the need to even ask that question.’
‘I’m sorry, Louise, but it’s standard procedure.’
‘Johnny, you don’t really think I could’ve done that, do you?
‘Not for a second, Louise. Just playing by the rules.’
The exception is dialogue between ranking officers or titled people and their staff. Omitting the sir, Your Lordship, Your Majesty, milady and the like would be unrealistic:
‘Twelve, sir. We’re expecting two more today.’
‘Any news on the Merton Street lead?’
‘Not yet, sir.’
‘Keep me informed, will you?’
‘Yes, sir.’
SOLUTIONS
- Use vocatives appropriately and sparingly.
- Speech tags and action beats are alternatives that you can bring into the mix.
- Trust your reader. If there are only two people in conversation, indicative nudges once in a while as to who’s speaking will be enough.
- Read ‘How to punctuate dialogue in a novel’ for guidance on how to punctuate vocative expressions.
Problem 7: Thoughts in speech marks
Speech marks (or quotation marks) have one function – to show the reader that a character is speaking out loud. While some recognized style guides allow for the use of speech marks to indicate thoughts, most professional editors and experienced writers don’t recommend this method because it’s confusing.
Some authors might be tempted to use a different speech-mark style to indicate a thought. Again, this is confusing. Your reader might assume that you’ve not edited for consistency.
Here’s an example in which dialogue and thought have become muddled:
“No way. Not until I have some guarantees.”
Jackson gripped the weapon and glanced left then right. He was surrounded by agents, all of them armed to the teeth.
‘Fuck fuck fuck. How the hell am I going to get out of this one?’ he thought.
SOLUTIONS
- Reserve speech marks for the spoken word and keep the style consistent.
- Render thoughts in italic or roman.
- Experiment by combining short present-tense italicized thoughts with past-tense free indirect style.
- Read ‘ How to write thoughts in fiction ’ for a more detailed analysis of how to show what characters are thinking.
- Read ‘3 reasons to use free indirect speech in your crime fiction’ (the principles apply across genres).
Problem 8: Thinking unlikely thoughts
If your character’s in the middle of an escape, a heist, great sex, or a mixed-martial arts smackdown, thoughts need to be handled with care to remain realistic. High-intensity scenes require rapid-fire thoughts otherwise the thinking becomes intrusive and moderates the pace of the action.
Here’s an extreme example of how things can go awry:
Gunfire sent her scrambling on her belly for the door.
Some writers use a character’s thoughts as a conduit for providing physical description. Take care with this. In reality, it’s rare for us to look in a mirror and notice our brown hair, green eyes or big feet. Instead, we’re more likely to frame those ideas in terms of criticism, appreciation or concern:
Compare these two examples:
|
Unlikely thought
|
Thought framed in criticism
|
|
Louise stopped in front of the mirror. Time to brush those blonde locks, she thought.
|
Louise stopped in front of the mirror. Christ, blonde really isn’t my colour, she thought.
|
- Read the character’s thoughts out loud. Would you articulate them internally in that situation?
- Think about your character’s emotional state – would they have time to think and, if so, what would be on their mind in that moment?
- Read ‘Unveiling your characters: Physical description with style’ for more tips on how to describe characters.
- Read ‘3 reasons to use free indirect speech in your crime fiction’ for more ideas about how to convey what’s going on in a character’s head.
Summing up
‘Dialogue isn’t a report of everything that characters say. It’s the compelling and noteworthy real-time, purpose-filled talk that plays out in front of the reader,’ writes Beth Hill (p. 157): The same can be said of thoughts.
Reality takes a nosedive when it comes to the novel because only a little of what people think and say in real life will drive a story forward. Most of it is dull.
Here’s Sol Stein (p. 113): ‘People won’t buy your novel to hear idiot talk. They get that free from relatives, friends, and at the supermarket. […] Some writers make the mistake of thinking that dialogue is overheard. Wrong! Dialogue is invented and the writer is the inventor.’
Invent dialogue and thoughts that show readers what is being felt (emotion) and what is happening (action).
Cited sources and other resources
- Stein on Writing. By Sol Stein. St. Martin's Press. 2014
- The Magic of Fiction, 2nd ed. By Beth Hill. Title Page Books. 2016
- Dialogue resources for authors and editors
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
Filter words are verbs that increase the narrative distance, reminding us that what we’re reading is being told by someone rather than experienced, or shown, through the eyes of the character.
Examples include noticed, seemed, spotted, saw, realized, felt, thought, wondered, believed, knew, decided.
I see more extensive filtering in books written by less experienced novelists who’ve not yet learned to trust their characters’ voices, who are uncomfortable about playing with devices such as free indirect style, or who are still learning the craft of injecting drama into narrative.
I’ve taken some examples from published fiction and introduced filtering so you can see the difference, and how by avoiding filter words the writers have brought immediacy to their narratives:
|
ORIGINAL UNFILTERED
|
FILTERED BY ME
|
|
When the dark mellowed, he shuffled inside and sank onto the seat that a long-dead troglodyte had hewn into the cave wall. The familiar coldness seeped through his trousers and into his flesh.
Roz Watkins, The Devil’s Dice, p. 1 |
When he saw that the dark had mellowed, he shuffled inside and sank onto the seat that a long-dead troglodyte had hewn into the cave wall. He felt the familiar coldness seeping through his trousers and into his flesh.
|
|
The address is typed on a sticker, the postmark a smudge of ink in the top right-hand corner.
Clare Mackintosh, Let Me Lie, p. 15 |
I notice the address and realize it’s typed on a sticker, the postmark a smudge of ink in the top right-hand corner.
|
|
Earlier that morning, she’d groaned at the invasive ringtone from her partner’s iPhone. […] How could such a small slab of silicone produce so much noise?
Val McDermid, Insidious Intent, p. 14 |
Earlier that morning, she’d groaned at the invasive ringtone from her partner’s iPhone. […] She wondered how such a small slab of silicone could produce so much noise.
|
Filter words – particularly when they’re used as a narrative staple – tap the reader on the shoulder and say, ‘You’re not in this book. Someone else is experiencing this.’ They’re a reminder that doing is being done.
Of course, we as readers know this to be true. Still, there’s nothing like immersing yourself in a character’s journey.
Here’s an extreme example I made up:
He recalled their most recent argument and felt himself shudder. He’d looked on as she’d screamed abuse at him, seen the spittle fly from her mouth. He’d felt sadness at first but that had turned to fear when he’d seen her pick up a knife from the table.
The text is horribly laboured – overly cluttered with doing being done. When confronted with a novel filled with filtering, readers will be tempted to skim, which means they might miss something crucial. A worst-case scenario is that they’ll give up because it’s not an enjoyable experience.
Now let’s tighten it up by removing the filter words:
He shuddered, recalling their most recent argument. At first, there’d been only sadness as she screamed abuse at him, spittle flying from her mouth, but that had turned to fear when she’d reached for the knife on the table.
We’ve lost none of the detail but now the prose is more emotionally immersive. We can better feel John’s predicament because we’re not repeatedly told that he’s doing the doing. It’s narration that feels less narrated.
When filter words add texture
I’m not suggesting you ban all filter words. When used intentionally they have a layering effect that can enrich a novel.
- You might want to pepper your narrative style with some telling filters to mix things up.
- Perhaps the narrative distance in much of the surrounding text is close and you want to ease the tension and pull the reader back.
- You might use filter words to introduce a different mood, for example, more enquiring or deliberative.
- You might even need them so that your prose makes sense – sometimes a character does realize or watch or think something, and we need to know that.
- Filter words can deepen character voice, especially in a first-person narrative.
The Mackintosh example above is in first person. I think my filtered version works; it’s just different. Or perhaps it would be stronger with only one of the filters. Either way, one might argue that it imparts a deeper sense of the character’s scouring the envelope for clues.
I still prefer Mackintosh’s approach because I like my crime fiction on the nose, but the experiment demonstrates that filter words aren’t wrong or right, but rather devices you can use to play with the reader’s experience of your story and the characters moving around within it.
Here’s an example from Philip Prowse’s Hellyer’s Trip, p. 194:
Prowse uses a filter word here: knew. He then follows through with free indirect style to close the narrative distance and take us right inside the character’s head while still maintaining a third-person viewpoint.
So let’s look at what happens when we remove ‘He knew’.
I think the unfiltered version works very well but it does change the feel of the writing. Gone is the sense of deliberation. All four sentences are immediate. To my ear, the rhythm accelerates. And although there’s a feel of telling with the inclusion of ‘He knew’ in the published version, there’s also an increased sense of despondency, as if the character has had time to think this over and arrive at this knowledge.
I mentioned character voice above. Here are two examples from Play Dead by David Rosenfelt:
Rosenfelt’s writing is tight. He never drops a beat. When he uses a filter word it’s with intention. Those who’ve read the Andy Carpenter series will know that this fictional attorney’s voice drips with a delicious acerbity, and the character thinks, acts and speaks with purpose.
When we’re told he realizes something it’s because the author wants us to have a sense of dawning awareness, not because he couldn’t be bothered to cast the sentence in a way that avoided it.
Most of the time, Rosenfelt avoids filter words: ‘I’m so pissed …’ not ‘I feel so pissed …’; ‘He spends most of the time …’ not ‘I listen to him …’. However, he chooses to tag ‘I don’t think’ onto the beginning of the final sentence rather than going with something like ‘My silent treatment isn’t bringing him to his knees.’ And, actually, the protagonist’s thinking is what deepens the voice and the immediacy.
Summing up
To keep your prose tight, look out for filter words that tell of doing being done. Then consider whether a gentle recast without them will improve your prose. How does the revised text make you feel? Is the meaning still clear? Is the mood you’re seeking evident?
If the prose feels more dramatic and immersive, you’ve done your novel and your readers a favour. If you lose something in the revision, like voice, mood or intention, reintroduce your filters at the appropriate points.
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
Visit her business website at Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader, say hello on Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, connect via Facebook and LinkedIn, and check out her books and courses.
Use them purposefully in your writing when they bring clarity, but remove them when they create clunk.
The fiction writer – and the fiction editor – who takes a formulaic approach to the treatment of adverbs is heading for trouble.
A note on form
Not all adverbs end in –ly (e.g. backwards, inside) and not all words ending in –ly are adverbs (e.g. deadly is an adjective and anomaly is a noun).
That’s one good reason not to eradicate all –ly words from your writing.
To work out whether a word or phrase is behaving adverbially, focus on what it’s modifying not on how it’s spelled.
Verb and adverbs – a quick refresher
A verb is a doing word; it describes a physical or mental action or state of being.
- He swam in the sea.
- That young boy believes in fairies.
- My throat hurts.
- She considered the question and responded accordingly.
- It appeared from nowhere.
- ‘It was a joke, you fool.’
An adverb is a word that describes a verb (just as an adjective describes a noun).
- To boldly go where no one has gone before.
- Mr Bradshaw died suddenly.
- He spoke eloquently.
- ‘James, sit there.’
- She blinked rapidly.
- Roy leaned backwards into the chair.
An adverbial phrase behaves in the same way but uses two or more words to describe the verb (or verb phrase).
- Jonas sat in silence.
- He laughed like a hyena.
- The guy’s been shot in the back.
- Maria stomps her feet in fury.
- We strolled under the light of the silvery moon.
Clunk: Telling us what we already know from dialogue
Here are four examples where the adverb (in bold) attached to the speech tag is redundant because the information in the dialogue does the same job:
- ‘Hand over the fifty thou by Thursday or I’m telling your wife,’ she said threateningly.
- ‘That’s your final warning, son,’ said Jake in a cautionary tone.
- ‘I mean, really, it’s a privilege to breathe the same air as you!’ he said gushingly.
- ‘Take it or leave it – I couldn’t care less,’ said John dismissively.
These aren’t rules but guidelines. Test it. Remove the adverb and read the sentence aloud. Is the intention still clear from the dialogue you’ve written? If so, great – you can lose the adverb. If it’s not, can you recast the dialogue? Consider the following:
- ‘Take it or leave it,’ said John.
- ‘Take it or leave it,’ said John dismissively.
- ‘Take it or leave it – I couldn’t care less,’ said John.
- ‘Take it or leave it – I couldn’t care less,’ said John dismissively.
In (1), dialogue and supporting speech tag seem a little flat. In (2), the adverb helps us to understand John’s mood. In (3), we lose the adverb but the mood intention is supplied by the additional dialogue. In (4), the adverb repeats the mood intention.
None of above four examples is grammatically incorrect, but (1) is possibly underwritten and (4) is definitely overwritten.
Context is everything though. If you’re writing a high-octane crime-thriller scene in which the pace is fast and furious, (1) might just be perfect, (2) and (3) would slow the reader down, and (4) would still be a non-starter.
Clunk: Telling us what we already know from the speech tag
Here are three examples where the adverb (in bold) is redundant because the verb (in italic) provides the same information:
- ‘I love you,’ she whispered softly.
- ‘Stop it at once!’ she yelled loudly.
- ‘I don’t understand. Are you sure that’s right?’ she asked questioningly.
‘Said’ is a rather delicious speech tag because it’s almost invisible. (For an examination of tagging, read: ‘Dialogue tags and how to use them in fiction writing’.)
Readers are so used to seeing ‘said’ that they slide over it without a glance. And that means they stay immersed in the conversation on the page, which if you’re writing dialogue is exactly where you want them.
Clunk: Telling us what we already know from the verb
Here are three examples where the adverb or adverbial phrase (in bold) is redundant because the verb (in italic) provides similar information in the narrative:
- Magne galloped quickly across the heath.
- She inched step by step down the narrow alley.
- He gasped breathily as Mark’s lips grazed his neck.
Slips like these can occur because the writer is still learning to trust their reader. They fear there are too few words or that the description isn’t rich enough. And sometimes writers just run away with themselves, so deeply are they immersed in the world they’ve created and what their characters are experiencing.
This is why drafting and redrafting are so important, and why a fresh set of professional eyes can give the writer courage. I hire people to check most of my own writing because I know that even when I’m writing educational non-fiction I’m so desperate to get my point across that I can sometimes end up in a right old tangle!
Self-editing is hard – professional editors know this. Don’t beat yourself up if you’re prone to double tells – you’re only human. Instead, cross-check your adverbs against your verbs to make sure you’re not repeating yourself.
Clunk: Dragging us away from immediacy
Some adverbs like suddenly, immediately and instantly can do the opposite of what's intended. Overuse can make the action less sudden, less instant. I cover this in detail in Why ‘suddenly’ can spoil your crime fiction: Advice for new writers.
In brief, these adverbs can act like taps on the shoulder that prevent the reader from moving through a story at the same pace as the character. The suddenness of the action is told to us first instead of being experienced by us.
Compare these examples. They demonstrate how removing the adverbs can leave the immediacy of events intact.
A damp mist had settled but he was snug enough. The parka would keep the edge off until the sun rose.
Suddenly, the phone trilled in his pocket, jolting him.
WITHOUT:
A damp mist had settled but he was snug enough. The parka would keep the edge off until the sun rose.
The phone trilled in his pocket, jolting him.
WITH:
Jimmy immediately slammed on the brake, fighting with the wheel as the car careened around the corner.
WITHOUT:
Jimmy slammed on the brake, fighting with the wheel as the car careened around the corner.
Purposeful adverbs
Adverbs, used well, can show motivation, indicate mood, and enrich our imagining of a scene.
I love books that tell it straight because every word pushes me forward. David Rosenfelt is a writer who never disappoints. His Andy Carpenter series features a tenacious lawyer with a dry wit.
The author’s prose is sharp as a knife. Does he use adverbs? Absolutely, though sparingly and they’re always purpose-filled.
|
‘Most of that time we’ve been in my house, which I’ve selfishly insisted on because that’s where Laurie is. Kevin had no objections, because it’s comfortable and because Laurie is cooking our meals.’
(Play Dead, p. 119. Grand Central Publishing; Reprint edition, 2009) |
MOTIVATION:
The adverb tells us about the emotional motivation behind Carpenter’s insistence (Laurie is his lover), which contrasts with Kevin’s motivation: convenience. |
|
‘I accept his offer of a glass of Swedish mineral water and then ask him about his business relationship with Walter Timmerman. He smiles condescendingly and then shakes his head.’
(New Tricks, p. 110. Grand Central Publishing; Reissue edition, 2010) |
MOOD:
Removing the adverb might lead us down the path of thinking that Jacoby, the smiler, is being congenial. He’s not. The scene is confrontational, though measured. |
|
‘Milo is digging furiously in some brush and dirt. The area has gotten muddy because of the rain, but he doesn’t seem to mind.’
(Dog Tags, p. 291. Grand Central Publishing; Reprint edition, 2011) |
SCENE ENRICHMENT:
The adverb enables us to imagine how manic the dog is – we can see his legs pumping, muck flying everywhere, perhaps some doggy drool swinging from the corners of his mouth. That single modifier enriches the narrative. |
Use adverbs when they help your reader understand more than they would have without them. A well-placed adverb or adverbial phrase will help you keep your prose leaner because it will nudge a reader towards imagining the action, the mood of the characters and what their intentions are.
If they’re repetitive clutter that add nothing we couldn’t have guessed, get rid of them. If the narrative or dialogue feels flat, head for a thesaurus and find alternative verbs that will bring your prose to life.
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
In a nutshell, free indirect speech offers the essence of first-person dialogue or thought but through a third-person viewpoint.
The character’s voice takes the lead, but without the clutter of speech marks, speech tags, italic, or other devices to indicate who’s thinking or saying what.
It’s a useful tool to have in your sentence-level toolbox because:
- It’s flexible and can add interest
- It can make for a leaner narrative
- It can deepen our understanding of a character
The table below shows three contrasting third-person narrative styles in action so you can see how free indirect speech works:
|
Indirect/reported
|
Rathbone thought Cumberbatch’s portrayal of Sherlock Holmes was excellent and decided it was time to hang up his deerstalker.
|
|
Direct/quoted
|
‘Time I hung up my deerstalker,’ said Rathbone. ‘That Cumberbatch chap’s doing a sterling job with Holmes.’
|
|
Free indirect speech
|
Time to hang up his deerstalker – that Cumberbatch chap was doing a sterling job with Holmes.
|
1. Flexibility and interest
Free indirect speech (FIS) is flexible because it can be blended seamlessly with other third-person narrative styles.
Let’s say you want to convey information about a character’s physical description, their experiences, and their thoughts – what they think and delivered in the way they’d say it.
You could use third-person objective for the description, third-person limited for the experience, and free indirect speech for some of the thought processes.
In other words, you have a single narrative viewpoint but styled in different ways. You’re not changing the viewpoint, but rather shifting the distance between the reader and the character. And that can make your prose more interesting.
Here’s an example from Val McDermid’s Insidious Intent (p. 14). She begins with a more distant third-person narrator who reports what had been on Elinor Blessing’s mind, and when. Then she shifts to free indirect speech (the bold text). This gives us temporary access to Blessing’s innermost thoughts – her irritation – and her lightly sweary tone, but still in the third-person:
|
It had been on her mind for days. The last thing on her mind as she let the oblivion of sleep overtake her, the first thought on waking.
Earlier that morning, she’d groaned at the invasive ringtone from her partner’s iPhone. Bloody cathedral bells. How could such a small slab of silicone produce so much noise? At this rate, she was going to end up as the Quasimodo of the A&E department. ‘Paula,’ she grumbled sleepily. ‘It’s my day off.’ |
Philip Prowse employs a similar shift in Hellyer’s Trip (p. 194):
2. A leaner narrative
FIS is a useful tool when you want to declutter.
Direct speech and thoughts are often tagged so that the reader knows who’s speaking/thinking:
- ‘Blah blah,’ she said.
- Blah blah, she wondered.
With regard to thoughts, there’s nothing wrong with a reader being told that a character thought this or wondered that, but tagging can be interruptive and render your prose overworked and laboured if that’s the only device you use.
Imagine your viewpoint character’s in a tight spot – a fight scene with an arch enemy. The pace of the action is lightning quick and you want that to be reflected in how your viewpoint character experiences the scene. FIS enables you to ditch the tags, focus on what’s going on in the character’s head, and maintain a cracking pace.
The opening chapter of Stephen Lloyd Jones’s The Silenced contains numerous examples of free indirect speech dotted about. Mallory is being hunted by the bad guys. She’s already disarmed one in a violent confrontation and fears more are on the way. Jones keeps the tension high by splintering descriptions of step-by-step action with free-indirect-styled insights into his protagonist’s deepest thought processes as, ridden with terror, she tries to find a way out of her predicament:
|
She tensed in the doorway, holding herself erect, terrified that by moving she would give away her position and feel the wet kiss of a blade, or bone-shattering impact of a hammer.
Another press of air lifted fronds of her hair from her face. Abruptly, she recalled the window she had found at the back of the house, open to the night. Of course. That was the source of the breeze. [...] Was there anything she had forgotten? The Nissan’s keys were in her right-hand pocket. She had the two books from the study. That was it. Reaching for the deadbolt, she carefully drew it back. Breathe in. Breathe out. |
Here’s an excerpt from Lee Child’s The Hard Way (p. 64). Child doesn’t use FIS to close the narrative distance. Instead, he opts to shift into first-person thoughts. Reacher is wondering if he’s been made, and whether it matters:
|
Reacher asked himself: did they see me? He answered himself: of course they did. Close to certainty. The mugger saw me. That was for damn sure. And these other guys are smarter than any mugger. [...] Then he asked himself: but were they worried? Answered himself: no, they weren’t. The mugger saw a professional opportunity. That was all.
|
Some might argue that this is a little clunkier than going down the FIS route, but perhaps he wanted to retain a sense of Reacher’s clinical, military-style dissection of the problem in hand.
If Child had elected to use FIS, it might have looked like this:
Had they seen him? Of course they had. Close to certainty. The mugger saw him – that’s for damn sure. And those other guys were smarter than any mugger. [...] But had they been worried? No, they’d seen a professional opportunity. That’s all.
It’s a good reminder that choice of narrative style isn’t about right or wrong but about intention – what works for your writing and your character in a particular situation.
3. Deeper insight into characters
A third-person narrator is the bridge between the character and the reader. As such, it has its own voice. If there’s more than one viewpoint character in your novel, we can learn what we need to know via a narrator but the voice will not be the same as when the characters are speaking in the first person.
FIS allows the reader to stay in third-person but access a character’s intimate world view and their voice. It closes the distance between the reader and the character because the bridging narrator is pushed to the side, but only temporarily.
That temporary pushing-aside means the writer isn’t bound to the character’s voice, state of mind and internal processing. When the narrator takes up its role once more, the reader takes a step back.
Furthermore, there might be times when we need to hear that character’s voice but the spoken word would seem unnatural:
- Perhaps they don’t have time to verbalize (a high-octane escape scene).
- Maybe they’re on their own and talking to themselves isn’t a known trait.
- Speaking out loud would give them away.
- Dialogue would seem forced because a character wouldn’t give voice to the words in real life.
FIS therefore allows a character to speak without speech – a silent voice, if you like.
Think about transgressor narratives in particular. If you want to give your readers intimate insights into a perpetrator’s pathology and motivations, but are writing in the third-person, FIS could be just the ticket.
Here’s an example from Harlan Coben’s Stay Close (chapter 25). Ken and his partner Barbie are a murderous couple bound together by sadism and psychopathy. Ken is preparing for the capture and torture of a police officer whom he believes is a threat:
|
The cop, Broome, entered the house. Ken wanted to curse, but he never cursed. Instead, he used his favorite word for such moments – setback. That was all this was. The measure of a man isn’t how many times he gets knocked down; it’s how many times he gets back up again. He texted Barbie to stay put. He tried to listen in but it was too risky. [...]
What more could any man want? He knew, of course, that it wouldn’t be that simple. He had compulsions, but even those he could share with his beloved. What was he waiting for? He turned back toward the house. |
This excerpt is from an audiobook. While listening, I could hear how the voice artist, Nick Landrum, used pitch to shift narrative distance.
The book’s entire narrative is in the third-person, but Landrum used a higher pitch when presenting the narrator voice. Ken’s dialogue, however, is in a lower pitch, and so is the free indirect speech of this character – we get to hear the essence of Ken even when he’s not speaking out loud.
If you’re considering turning your novel into an audiobook, FIS could enrich the emotionality of the telling, and the connection with your listener.
A closer look at narrative distance
To decide whether to play with free indirect speech, consider narrative distance and the impact it can have on a scene.
Look at these short paragraphs, all of which convey the same information. All are grammatically correct but the reader’s experience is different because of the way in which the information is given, and by whom.
|
1
|
Dave glanced at the guy’s hand and spotted the absence of the signature tattoo. It forced him to consider the integrity of the intel he’d been given. Again. And it bothered him.
Third-person: A narrator reports the situation and what the character’s thinking. Most distant. There’s shallower emotional connection between the reader and the viewpoint character. The narrator’s voice is more clinical and dominates. |
|
2
|
Dave glanced at the guy’s hand and spotted the absence of the signature tattoo. ‘Christ,’ he muttered under his breath, not for the first time questioning the integrity of the intel he’d been given.
Third-person: A narrator reports the situation and most of what the character’s thinking. First-person: A character reports a little of what he’s thinking. Less distant. The dialogue burst gives voice to the character, which introduces tension. |
|
3
|
Dave glanced at the guy’s hand and spotted the absence of the signature tattoo. Christ, he thought. Maybe my intel’s been compromised yet again.
Third-person: A narrator reports the situation. First-person: A character reports what he’s thinking. Closer. Readers might find italic thoughts and tags disruptive, or believe that such well-structured thoughts aren’t authentic. |
|
4
|
Dave glanced at the guy’s hand and spotted the absence of the signature tattoo. ‘Christ, maybe my intel’s been compromised again,’ he muttered.
Third-person: A narrator reports the situation. First-person: A character shares his concerns out loud. As close as (3) above. Dialogue might seem forced, unnatural, spoken purely to help the reader understand what the problem is. |
|
5
|
Dave glanced at the guy’s hand. No signature tattoo. Christ, had his intel been compromised again?
Third-person: A narrator reports the situation, and a character reports what he’s thinking via free indirect style. We’re right inside the character’s head but there’s no cluttering italic, speech marks or tagging. The free indirect style feels natural precisely because it’s rendered in the third-person and yet it holds the intimacy of a first-person experience offered in (3) and (4). |
|
6
|
I glanced at the guy’s hand. There was no signature tattoo. Christ, had my intel been compromised again?
First-person: A viewpoint character reports the situation and what he’s thinking. Closest. We’re right inside the character’s head, there’s no clutter, and the narrative feels completely natural. However, this only works if you’ve chosen a first-person narrative for this viewpoint character throughout the book, which you might find limiting. |
Consider the following examples in relation to the table above:
- Is the scene fast-paced and do you want to keep your sentences lean and keen to reflect that pace? The viewpoint character might not have the mental space to articulate fully rounded thoughts or speech because they’re in a fight or trying to escape. In that case, the free indirect style of 5 might suit you. So might 6 if you’re writing in the first person.
- Is the viewpoint character hiding, observing something going on but invisible to those around them? If they feel in command but are taking care to remain unnoticed, 2 might offer you the required tension while enabling you to retain tight control over the narrative via a narrator.
- If your character has the space to think but is panicking, you might prefer 3 or 4. Anxiety can lead people to articulate complex thoughts, even voice them out loud, in the search for clarity.
- If your viewpoint character’s personality is cooler, more detached, you might prefer the emotional disconnectedness of 1.
- And if you’re writing in the third-person, but want the reader to feel intimately connected with the viewpoint character, you might swing back to the free indirect style of 5.
Wrapping up
FIS is used across genres, but I think it’s a particularly effective tool in crime writing because of its ability to simultaneously embrace brevity and communicate intimacy.
Jon Gingerich sums up as follows: ‘Free Indirect Discourse takes advantage of the biggest asset a first-person P.O.V. has (access) and combines it with the single best benefit of a third-person narrative (reliability). It allows the narrator to dig deep into a character’s thoughts and emotions without being permanently tied to that person’s P.O.V. Done correctly, it can offer the best of both worlds.’
If you haven’t yet played with it, give it a go, especially if you’re looking for ways to trim the fat.
Further reading
- ‘A beginner’s guide to narrative point of view in crime fiction.’ Louise Harnby, 2018
- ‘The Benefits of Free Indirect Discourse.’ LitReactor, 2012
- Hellyer’s Trip by Philip Prowse. Kernel Books, 2018
- Insidious Intent by Val McDermid. Little, Brown, 2017
- Stay Close by Harlan Coben. Whole Story Audiobooks, 2012
- The Hard Way by Lee Child. Bantam Press, 2006
- The Silenced by Stephen Lloyd Jones. Headline, 2018
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
Visit her business website at Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader, say hello on Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, connect via Facebook and LinkedIn, and check out her books and courses.
I’m not suggesting writers eradicate it, but rather use it judiciously and with intention.
There’s one word that great crime writers put on the page with care – suddenly. However, many new or developing writers struggle to leave it out.
Two reasons for overuse stand out:
- The writer is trying to counter wordiness
- The writer doesn’t realize their existing words have done the job
I’ve grabbed a handful of crime fiction from my own bookshelves, and taken examples from these books to show how suddenly-free writing can be more immediate and immersive.
1. Countering wordiness
Some developing writers record every nod, every furrowed brow. All that mundane stuff happens in real life. And in the movies we get to see it played out onscreen. That doesn’t mean it all needs to go into a novel.
Readers don’t behave like viewers. When I’m watching a film I expect to be spoon-fed to a degree – dialogue, facial expression, action, and a healthy dollop of incidental music to tell me who’s feeling what and why.
The reason it works with film is because a chunk of that stuff happens simultaneously, and even I, impatient soul that I am, don’t get bored.
When I’m reading a book, my brain works differently. I don’t want all that stage direction. Too much of it distracts me and that’s when I’m most likely to lose interest.
When a new writer hasn’t learned the art of crafting the story so that there are just enough nudges to keep the narrative rich, but not so many that it becomes tedious, suddenly rears its head. Suddenly becomes an apology for overwriting – an exciting reward for sticking around.
Only it doesn’t work. It’s just one more word on the page that the reader doesn’t need.
Solution: Keep your crime writing lean
Not every writer wants to strip their writing back to the bare bones but ask yourself whether you’ve introduced a sentence with Suddenly purely to reengage the reader.
If so, tighten up the preceding narrative so that you don’t lose them in the first place. Less is sometimes more.
Example
Here’s a scene from Tell No Lies by Gregg Hurwitz, featuring the protagonist, Daniel Brasher (p. 393):
|
He was ushered into a dank room with a stall terminating in a shield of ballistic glass that looked onto the mirror image of a facing stall. A coaster-size speaking hole in the glass rendered jailhouse phones unnecessary.
He waited, counting the seconds, working to stay calm. A metallic boom announced the opening of an out-of-sight metal door [...] |
A less experienced writer might have been tempted to overwork the preceding description and the line conveying Daniel’s anxiety ... and that could have led to a Suddenly barging its way onto the starting blocks of the final sentence to drag the reader out of the protagonist’s head and back into the external action.
It could have gone like this:
He waited, counting the seconds, working to stay calm. Sweat dripped from his forehead, ran down his back and soaked his shirt. He massaged his temples to stave off the growing panic and raked a clammy hand through his damp hair. Just relax, he thought. You’re in control.
Suddenly, a metallic boom announced the opening of an out-of-sight metal door ...
Instead, Hurwitz has given us just enough to know that our protagonist is fretful. We hear the metallic boom in the same moment Daniel does. We imagine how it might make him jump. There are 58 words instead of 114.
And the writing in the shorter, published example is tighter, the tension higher. The boom comes suddenly, but Hurwitz doesn’t tell us so. He doesn’t need to.
2. Redundancy – the verb’s already done the work
Even those novice writers who’ve conquered their noisy narrative can still be tempted to nudge unnecessarily with suddenly.
I see this most often in the following scene types:
- Fights: Suddenly, the masked man launched himself forward and crashed into Jake.
- Realizations: Suddenly, it dawned on her. It’d been staring her in the face all along.
- Emotional shifts: Suddenly, Ash’s face lit up with excitement.
- Grisly action: Suddenly, the woman’s torso exploded.
- Unexpected sounds: The phone trilled suddenly from his inside pocket.
- Shock events: Suddenly, Emma slammed on the brakes and the car skidded to a halt.
Certainly, writers who use suddenly are doing so with good intention – to give the reader a now-nudge. However, in most cases it’s unnecessary to convey immediacy and adds nothing to the narrative.
In the above examples, the immediacy is rendered perfectly with the verbs launched, dawned, lit up, exploded, trilled and slammed.
By adding suddenly into the mix, the reader is pulled out of the story, as if the author has tapped them on the shoulder and whispered, ‘Hey, you, something big’s coming. Just so you know. Right then, as you were. Carry on reading.’ That’s an interruption – the opposite of what the writer intended.
Now the reader’s no longer moving at the same pace as the character. They’re one step ahead rather than immersed in the moment.
Solution: Test the sentence out loud
Say it first with suddenly, then without. Ninety per cent of the time, the slimline version will work better. When that’s the case, hit the delete button.
- Fights: The masked man launched himself forward and crashed into Jake.
- Realizations: Then it dawned on her. It’d been staring her in the face all along.
- Emotional shifts: Ash’s face lit up with excitement.
- Grisly action: The woman’s torso exploded.
- Unexpected sounds: The phone trilled from his inside pocket.
- Shock events: Emma slammed on the brakes and the car skidded to a halt.
Published suddenly-free examples
Here are some published examples for comparison. None of the authors felt the need to nudge the reader into immediacy.
|
SHOCK EVENT AND FIGHT
He was ten meters away when Candy burst out, her raised fist firing muzzle flares. [...] He scissor-kicked for her Achilles, but she leapt over him, her hand swinging to aim as he popped to his feet. He lunged inside her reach, grabbing the gun as it grazed his cheek. Her hand blocked the rising shotgun. Gregg Hurwitz, Orphan X, p. 340 |
|
GRISLY ACTION
Cory found his hands around her neck. He pushed her up against the wall and squeezed with everything he had. She put up a good fight, he had to give her that. Kicked and flailed about, but he didn’t let go, didn’t stop squeezing. Not until she slid down the wall and crumpled into a heap on the floor. Linwood Barclay, Parting Shot, p. 376 |
The Barclay example is particularly interesting. The narrative point of view in this chapter is that of the antagonist. From his perspective, the violence is almost mundane, which renders the scene all the more horrific for the reader.
A now-nudge in this paragraph wouldn’t have been just superfluous; it would have countered the perversity of our tension being heightened through being forced to immerse ourselves in Cory’s psychosis.
When suddenly works a treat
Suddenly-free isn’t a rule. Don’t ban it from your novel! There are times when it works beautifully:
- There were ten of them, all big, corralling the guy into the corner. Pip watched, feeling suddenly vulnerable.
In this made-up example, the inclusion of suddenly subtly changes our perspective of Pip’s situation. There's a subtle immediacy to his discomfort has emerged only now, that in the seconds before he’d watched bu not felt threatened.
And so it’s not that suddenly does or doesn’t work. Rather, it depends on the writer’s intention.
Your turn ... how do you maintain tension with minimal interruption? Are there particular adverbs you use with caution?
If you'd like to access more tips and resources for self-publishers, visit my resource centre. Try these in particular:
She is an Advanced Professional Member of the Chartered Institute of Editing and Proofreading (CIEP), a member of ACES, a Partner Member of The Alliance of Independent Authors (ALLi), and co-hosts The Editing Podcast.
- Get in touch: Louise Harnby | Fiction Editor & Proofreader
- Connect: Twitter at @LouiseHarnby, Facebook and LinkedIn
- Learn: Books and courses
- Discover: Resources for authors and editors
BLOG ALERTS
TESTIMONIALS
Dare Rogers
'Louise uses her expertise to hone a story until it's razor sharp, while still allowing the author’s voice to remain dominant.'
Jeff Carson
'I wholeheartedly recommend her services ... Just don’t hire her when I need her.'
J B Turner
'Sincere thanks for a beautiful and elegant piece of work. First class.'
Ayshe Gemedzhy
'What makes her stand out and shine is her ability to immerse herself in your story.'
Salt Publishing
'A million thanks – your mark-up is perfect, as always.'
CATEGORIES
All
Around The World
Audio Books
Author Chat
Author Interviews
Author Platform
Author Resources
Blogging
Book Marketing
Books
Branding
Business Tips
Choosing An Editor
Client Talk
Conscious Language
Core Editorial Skills
Crime Writing
Design And Layout
Dialogue
Editing
Editorial Tips
Editorial Tools
Editors On The Blog
Erotica
Fiction
Fiction Editing
Freelancing
Free Stuff
Getting Noticed
Getting Work
Grammar Links
Guest Writers
Indexing
Indie Authors
Lean Writing
Line Craft
Link Of The Week
Macro Chat
Marketing Tips
Money Talk
Mood And Rhythm
More Macros And Add Ins
Networking
Online Courses
PDF Markup
Podcasting
POV
Proofreading
Proofreading Marks
Publishing
Punctuation
Q&A With Louise
Resources
Roundups
Self Editing
Self Publishing Authors
Sentence Editing
Showing And Telling
Software
Stamps
Starting Out
Story Craft
The Editing Podcast
Training
Types Of Editing
Using Word
Website Tips
Work Choices
Working Onscreen
Working Smart
Writer Resources
Writing
Writing Tips
Writing Tools
ARCHIVES
July 2024
June 2024
May 2024
April 2024
March 2024
October 2023
August 2023
July 2023
June 2023
May 2023
April 2023
March 2023
January 2023
December 2022
November 2022
October 2022
September 2022
August 2022
July 2022
June 2022
May 2022
April 2022
March 2022
February 2022
January 2022
December 2021
November 2021
October 2021
September 2021
August 2021
July 2021
June 2021
May 2021
April 2021
March 2021
February 2021
January 2021
December 2020
November 2020
October 2020
September 2020
August 2020
July 2020
June 2020
May 2020
April 2020
March 2020
February 2020
January 2020
December 2019
November 2019
October 2019
September 2019
August 2019
July 2019
June 2019
May 2019
April 2019
March 2019
February 2019
January 2019
December 2018
November 2018
October 2018
September 2018
August 2018
July 2018
June 2018
May 2018
April 2018
March 2018
February 2018
January 2018
December 2017
November 2017
October 2017
September 2017
August 2017
July 2017
June 2017
May 2017
April 2017
March 2017
February 2017
January 2017
December 2016
November 2016
October 2016
September 2016
June 2016
May 2016
April 2016
March 2016
February 2016
January 2016
December 2015
November 2015
October 2015
September 2015
July 2015
June 2015
May 2015
March 2015
February 2015
January 2015
November 2014
October 2014
September 2014
August 2014
July 2014
June 2014
March 2014
January 2014
November 2013
October 2013
September 2013
August 2013
June 2013
February 2013
January 2013
November 2012
October 2012
September 2012
August 2012
July 2012
June 2012
May 2012
April 2012
March 2012
February 2012
January 2012
December 2011
|
|
|













































































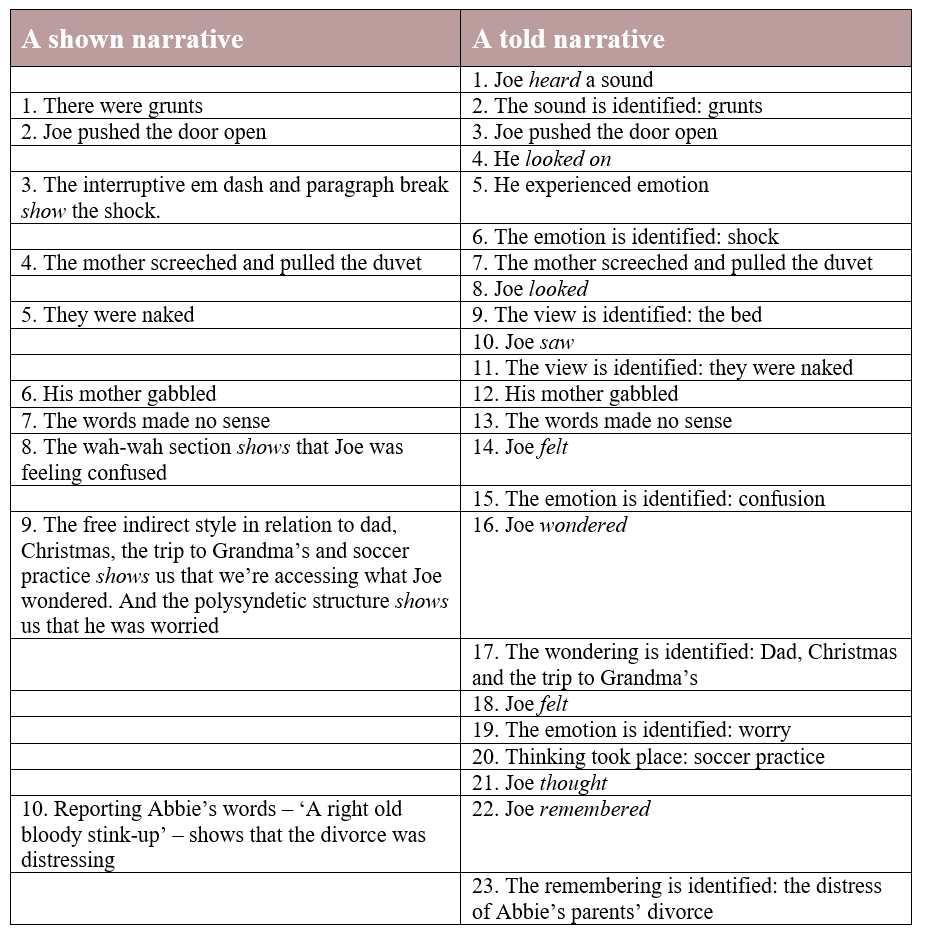












































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed





